What Is Agile Model in SDLC: The Guide on Software Development Methodology
Updated 18 Jan 2024
15 Min
1986 Views
Complex and sophisticated solutions are most often built using the Agile methodology and within the framework of the so-called Agile software development life cycle (SDLC). It is a methodology for architecting digital solutions which provides a more flexible approach for product creation, decreases the time-to-market, and allows simplified implementation of dynamic client requirements.
Agile SDLC is nowadays one of the most widely-applied approaches, and the statistics gathered by our team define its popularity:
- 71% of companies are using the Agile SDLC methodology.
- Agile applying has helped 98% of companies to successfully complete and enhance software development projects.
- 60% of companies receive increased revenue after adopting Agile.
- 80% of federal IT projects were accomplished using Agile.
- The failure rate of products built with software development life cycle Agile model is 8%, which is an extremely low indicator for this industry.
In this article, we will look at the concept, peculiarities, benefits, and phases of the Agile model SDLC.
What Is Agile Methodology in SDLC and Its Benefits
SDLC Agile methodology is an approach allowing to organize a project by dividing it into multiple stages. It implies continuous partnership with stakeholders and regular enhancements at every phase. The SDLC is often called a framework for projecting, creation, testing, management, and delivery of ensured tech services. Using the SDLC simplifies the process of defining the current phase developers work on, which resources are necessary, and what are the following directions to fulfill the project.
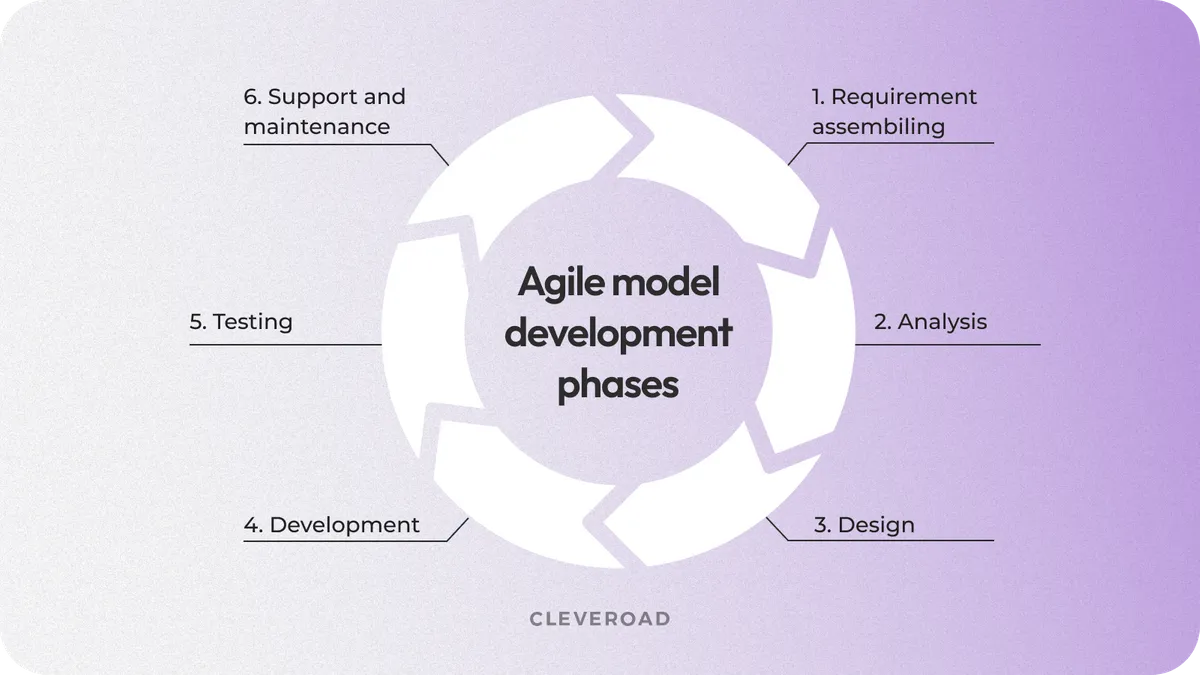
Agile SDLC example
Agile SDLC model main values are described in Agile Manifesto. Let’s review them in detail:
- People and interaction are more significant than processes and instruments
- Operating software is more important than thorough documentation
- Partnership with clients is more prioritized than agreeing on the contract terms
- Positive perception of changes is more significant than complying with the initial plan
Agile Manifesto also contains methodologie’s main principles, that include:
- Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software
- Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer's competitive advantage
- Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale
- Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project
- Build projects around motivated individuals
- The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation
- Working software is the primary measure of progress
- Agile processes promote sustainable development
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility
- Simplicity— the art of maximizing the amount of work not done— is essential.
- The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams
- At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly
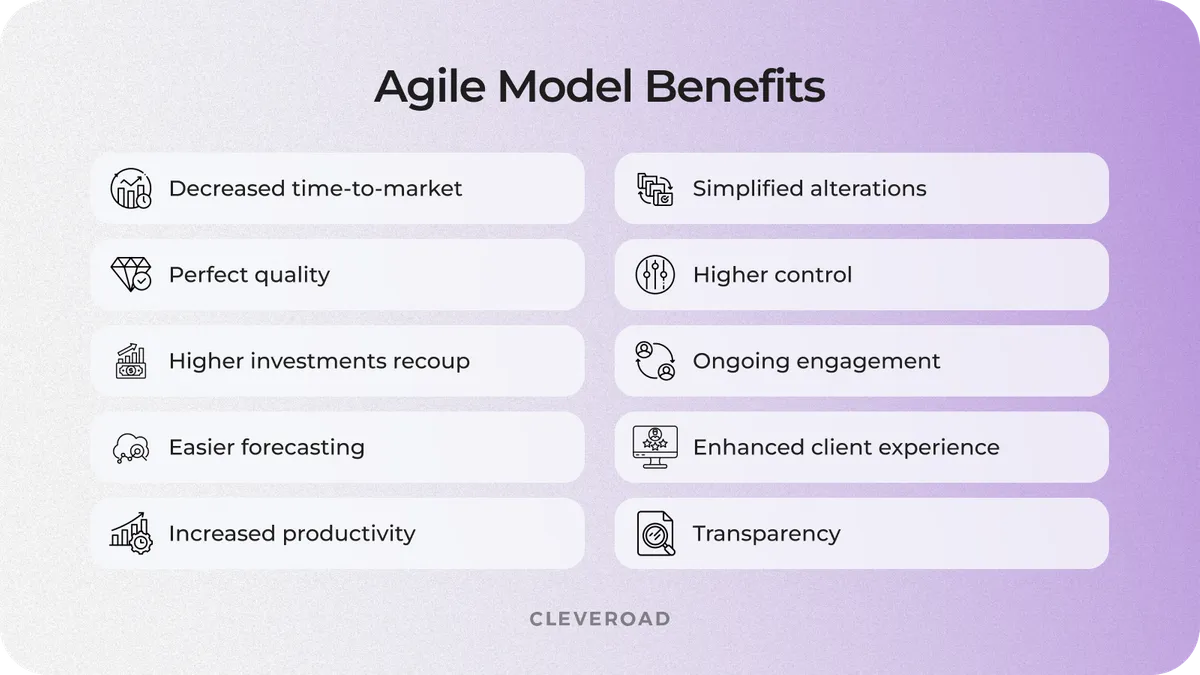
Benefits of Agile SDLC
Agile SDLC process offers various benefits that contribute to its popularity and effectiveness in modern software development.
Here are some key advantages of Agile SDLC:
- Faster time-to-market. Agile's iterative approach and shorter development cycles enable quicker releases of functional product increments. This rapid delivery allows businesses to get their products to market faster, ensuring a competitive edge and the ability to adapt swiftly to market changes.
- Improved quality. Agile SDLC methodologies emphasize continuous testing and integration throughout development. This constant focus on quality leads to early detection and resolution of defects. By addressing issues promptly, Agile ensures that the final software product is of higher quality and aligns better with user expectations.
- Customer satisfaction. Agile method SDLC prioritizes customer collaboration and values the regular delivery of valuable software. This approach ensures that customer feedback is actively incorporated throughout the development cycle, resulting in a product that better meets user needs. The emphasis on customer satisfaction contributes to long-term positive relationships.
- Increased stakeholder engagement. Agile in SDLC promotes frequent interactions with stakeholders, ensuring their active involvement throughout the project. This continuous engagement leads to better alignment with stakeholder expectations, as their feedback is considered and integrated into the ongoing development process. It fosters a collaborative relationship between development teams and project stakeholders.
- Flexibility and adaptability. SDLC Agile methodology allows flexibility in adapting to changing requirements and priorities. This adaptability is crucial, accommodating modifications even in the later stages of development. The Agile framework recognizes that requirements can evolve, and the ability to make adjustments ensures that the final product remains aligned with business needs.
Agile SDLC Techniques and Tools
Let's dive into the basics of Agile SDLC methodology techniques and tools that power this model's collaboration and efficiency.
Agile methodology techniques
Every SDLC methodology can be described as adaptive or predictive. The Agile model in SDLC relates to the adaptive group, whereas Waterfall, V-shaped, Iterative, and Spiral methodologies refer to the predictive model. Each of them is suitable for specific cases allowing to comply with a row of development requirements and satisfy users’ needs. Let’s observe the described models:
V-shaped SDLC Model
This approach is founded on the Waterfall model. The name “Waterfall” directly describes a building process, which is like a smooth stream, which means that tech-savvy specialists gradually complete each phase of the SDLC. Each step is finished with testing, and developers proceed to the following one only when the current phase is fully accomplished. The V-shaped SDLC model doesn’t ensure flexibility in changing requirements and making edits in contrast with the Agile software life cycle, so it brings certain complexities in taking a step back and integrating changes.
Iterative methodology
Its main peculiarity is the fact that this model may be used even without the complete list of requirements or if it’s dynamic. To begin the product development process, the functional part is only required. The row of requirements may be widened within the development flow. The iterative methodology involves the list of phases described above. The process is repetitive and provides the opportunity to enhance the software with every new version for each cycle. This model should be integrated prudently, or it may result in excessive alterations quickly draining development resources.
Spiral SDLC Model
This model puts a premium on assessing risks. The entire creation process is split into smaller stages for the team to complete. This may be a disadvantage, as there’s a chance of unnecessarily wasting time and money in case the software is new, and the accomplished project doesn’t require thorough documentation. In addition, the spiral model may also cost small and low-risk projects a fortune, which is also a considerable disadvantage.
Agile methodology tools
The Agile SDLC model relies on various tools to facilitate collaboration, communication, and project management. Here are some common tools used in Agile methodology:
- Jira. Jira is a popular project management tool that supports Agile SDLC methodologies. It helps teams plan, track, and manage their work by providing features for backlog prioritization, sprint planning, and issue tracking.
- Trello. Trello is a visual collaboration tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to organize tasks and projects. It's a simple yet effective tool for Agile teams to manage their work and workflow.
- Asana. Asana is a versatile project management tool that supports Agile model of SDLC. It allows teams to create tasks, assign them, set due dates, and track the progress of work.
- VersionOne. VersionOne is a comprehensive Agile project management tool that covers various aspects, including backlog management, release planning, and reporting. It is particularly useful for large-scale Agile projects.
- Confluence. Confluence, often used in conjunction with Jira, is a collaboration tool that helps teams create, share, and collaborate on project documentation. It supports the Agile principle of valuing working software over comprehensive documentation.
- Git. Git is a distributed version control system widely used in Agile SDLC model for managing source code changes. It allows teams to collaborate on code and track changes efficiently.
- Slack. Slack is a team collaboration platform that facilitates communication and information sharing among team members. It supports real-time messaging and file sharing, promoting quick and efficient collaboration between all team members.
These tools cater to different aspects of SDLC Agile model, providing support for project planning, task management, collaboration, and version control. The choice of tools depends on the specific needs and preferences of the Agile team.
Traditional Waterfall Vs. Agile: Which Methodology Should You Choose?
Due to the fact that the Agile SDLC process is frequently compared to the Waterfall model, we’ve prepared a detailed studying of those two methodologies below:
Agile
Pros
- Flexibility to comply with adaptive market and user requirements
- The space for a creative problem-solving approach
- Optimized resource allocation
- Regular updates and higher client satisfaction
- Rigid cadence, deadline adaptiveness
Cons
- Obscure planning may result in the unforeseen final result
- Receptive to a lack of concentration and responsive reactions within sprints
- Unremitting pace
- Inaccurate testing takes a chance in releasing a product with bugs
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
The Agile SDLC model ensures the most efficient practices among development environments. Certain risks of a project may be cut down as the output of specialists is monitored betimes and continuously within the process. | Agile may be quite simple at first glance, yet, in practice, this methodology isn’t the easiest one. Developers have to contribute higher commitment and be experienced when applying this approach. |
Scale and complex projects require more creativity and involve changing requirements, which is possible to implement with SDLC phases Agile. | With this approach, it may be challenging to make predictions concerning the final result. |
Opportunity to integrate alterations despite what stage is in progress now. | The Agile lifecycle model can’t be beneficial without constant collaboration and frequent communication among the team and with the client. |
Due to the fact that developers keep in touch with each other, it allows coming up with the most successful and efficient ideas, which positively impacts the final product quality. | Agile methodology SDLC is an extremely tense approach for both developers and users. For teams who implement several projects simultaneously, it may bring certain complexities. |
This methodology helps to decrease 'silos' commonly arise within project 'teams' - issues reducing the final quality result conditioned by the lack of united work. | An imprecise blueprint of the final product makes it difficult to obtain high engagement from the side of stakeholders at the early phase. |
Less repetitive alterations with SDLC Agile methodology, as all the issues and changes can be fixed and completed within the sprint. | SDLC and Agile complicate the interaction between the customer and the development team, as the first side is interested in what specialists are getting paid for as soon as possible. It may be complex to calculate deadlines and costs due to the inexactness of requirements. |
By applying special instruments, (boards, charts, Kanban tables, others) it can be simpler to track, manage, direct the development flow and make sure that everything is done in time. | Agile methodology life cycle makes it difficult to set deadlines. Large-scale projects can involve a row of components, and clients may reject the time period necessary for the project implementation. |
Waterfall
Pros
- Reduced “scope creep”
- A final software meeting all the requirements
- Easier dividing of roles and responsibilities
- More seldom updates accurately rolled out and provided to the market
- Set project plans and deadlines
Cons
- No flexibility when the specification document is ready
- Fewer opportunities to implement changes
- No sticking to innovations appearing on the market
- Too much time for bugs detection as testing is conducted only when the entire project is accomplished
- The change operation process is bureaucratic
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
On accurately-structured projects, Waterfall can ensure what the final result will be. | For large-scale projects, it is difficult to prepare early-stage plans, as there are lots of elements that have to be provided in advance. |
As the roles and responsibilities are divided at the initial stage, team members don’t have to obligatory be gathered in one office, as everyone knows the set tasks and scope of work. | There’s no opportunity to check the output before the project is fully accomplished, so developers have to keep in touch in order to maximize the software quality and meet the client’s expectations. |
For projects requiring multiple interfaces and dependencies outside of the elementary software creation, Waterfall ensures the necessary instruments allowing to model and manage these. | Risk is commonly raised with Waterfall, as the incorrect planning decreases the software quality, and this methodology makes it difficult to implement changes. This condition, accompanied by the high cost of Waterfall projects, is a substantial disadvantage. |
The Agile methodology in SDLC is more spread than the Waterfall nowadays. Nonetheless, the first methodology is suitable for small teams and startups engaging fewer teammates in projects. As client requirements meeting is the primary aim for developers, the Agile development cycle ensures flexibility to comply with dynamic needs. In case the project comprises set deadlines, stable requirements, and a limited budget, the Waterfall methodology is the beneficial option to adopt.
To explain the Agile software development life cycle model and its difference between the Waterfall one, let’s compare these two approaches at the illustration below:
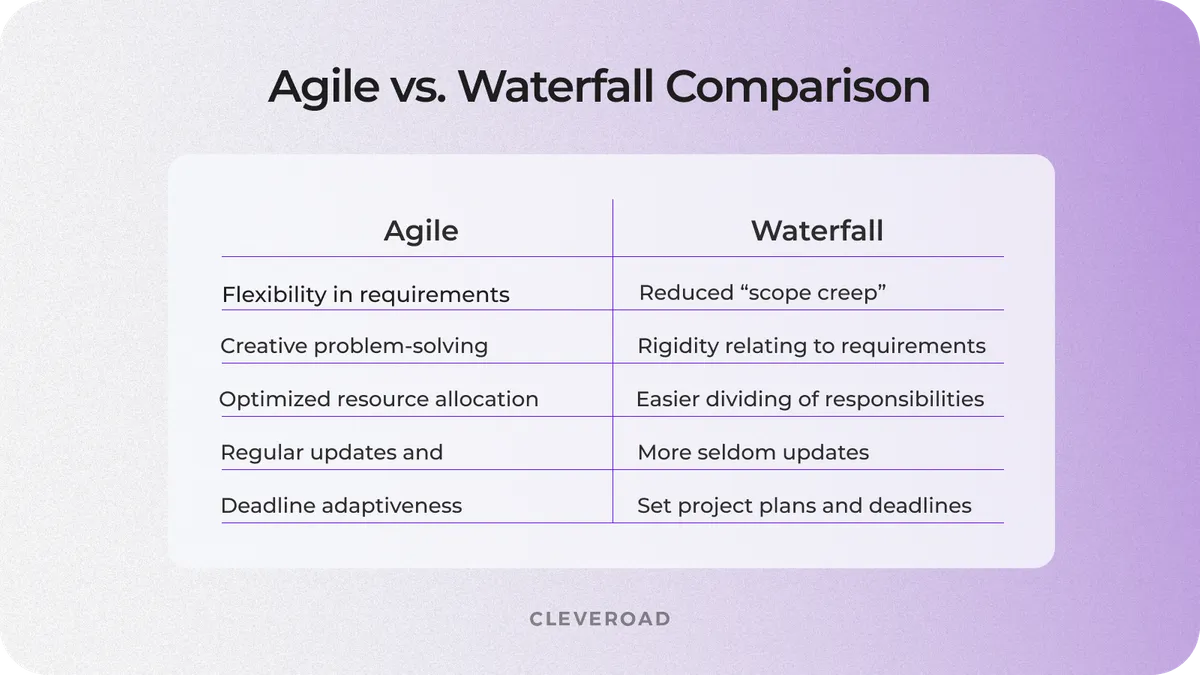
Comparing Agile and Waterfall models
Agile SDLC Process in 6 Phases
Due to the high flexibility level of the Agile methodology SDLC, its model is equally well suited to startups, innovative projects, as well as already established ones, like large-scale businesses and enormous corporations. In order to implement Agile SDLC process flow into your business, you may check the hints described below:
1. Prepare for the migration entirely
The fundamental step to take in terms of the SDLC Agile method transition is to notify and train your development team in the new architecture approach. To start the integration, you may find an illustration of the Agile model in SDLC with examples to share and describe it with your team so that they are aware of the basics.
Besides, it concerns not only tech specialists, managers, and other company members. Your customer base and other stakeholders should be informed that your team has moved to the leverage of SDLC in Agile model. Continuous partnership with your stakeholders is a significant point within the life cycle of Agile methodology, so they should also be notified.
2. Comprehend the Agile values and principles
Before migrating to the Agile life cycle model, the team and you should precisely study its manifesto for further application in the internal business workflow. Bring this topic to team meetings to discuss the company’s values, changes in them, and further methodology for developing follow-up projects together.
To illustrate, your employees and managers have to adapt to the SDLC Agile methodologies where they are aware of all the project details from its beginning. Mind that the transition process requires patience, as concentrating on the general plan and overall requirements may be unaccustomed for your development team.
Why is this process worth it? Experienced software development teams with adopted Agile and SDLC approaches reach their project targets 21% more regularly than inexperienced ones.
3. Select the suitable Agile framework for your team
Agile methodology in the software development life cycle will become a profitable and efficient approach if you choose the suitable framework for your team according to its workflow, scale, project complexity, requirements, targets, and needs. Here are the 7 most used frameworks for completing software development life cycles, including Agile development to pick from:
- Scrum: Agile framework that organizes work into fixed-length iterations called sprints, usually lasting 2-4 weeks. It employs key roles, including a Product Owner who prioritizes features and a Scrum Master who facilitates the process. Scrum emphasizes adaptability and regular team collaboration.
- Lean: Agile methodology drawing from Lean manufacturing principles, aiming to eliminate waste and enhance efficiency. Prioritizes delivering maximum value to customers with minimal resources. Lean focuses on continuous improvement, customer feedback, and timely delivery of valuable features.
- Kanban: Visual framework for managing work on a Kanban board. Emphasizes continuous and smooth workflow by visualizing tasks on cards that move through different stages. Allows teams to adapt to changing priorities and optimize processes based on real-time feedback.
- Crystal: Family of Agile methodologies tailored to a project's unique characteristics. Emphasizes the importance of people, interactions, and communication. Crystal methods are flexible and can be adapted based on the project's specific needs, promoting a collaborative and adaptive development.
- Extreme Programming (XP): Agile framework strongly emphasizes producing high-quality software. Incorporates practices such as pair programming, test-driven development (TDD), continuous integration, and frequent releases. Aims to improve software responsiveness to changing requirements.
- Feature-Driven Development (FDD): Iterative and incremental Agile methodology with a feature-centric approach. Particularly suited for large-scale projects. Emphasizes creating well-defined features, domain object modeling, and regular client collaboration to deliver tangible results.
- Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM): Agile framework focusing on rapid and iterative development. Places importance on fitness for business purposes and collaboration between business stakeholders and development teams. Provides a structured approach to project management focusing on delivering real business value.
These frameworks offer diverse approaches to Agile and SDLC, catering to various project requirements and team dynamics. The choice often depends on the project's size and organizational preferences.
4. Fill and optimize a product backlog
The further tactics refer to Scrum projects built with SDLC for Agile. You should cooperate with stakeholders to build a backlog of potential functionality and essential user stories for the software. Here's the example of product backlog for Agile SDLC model:
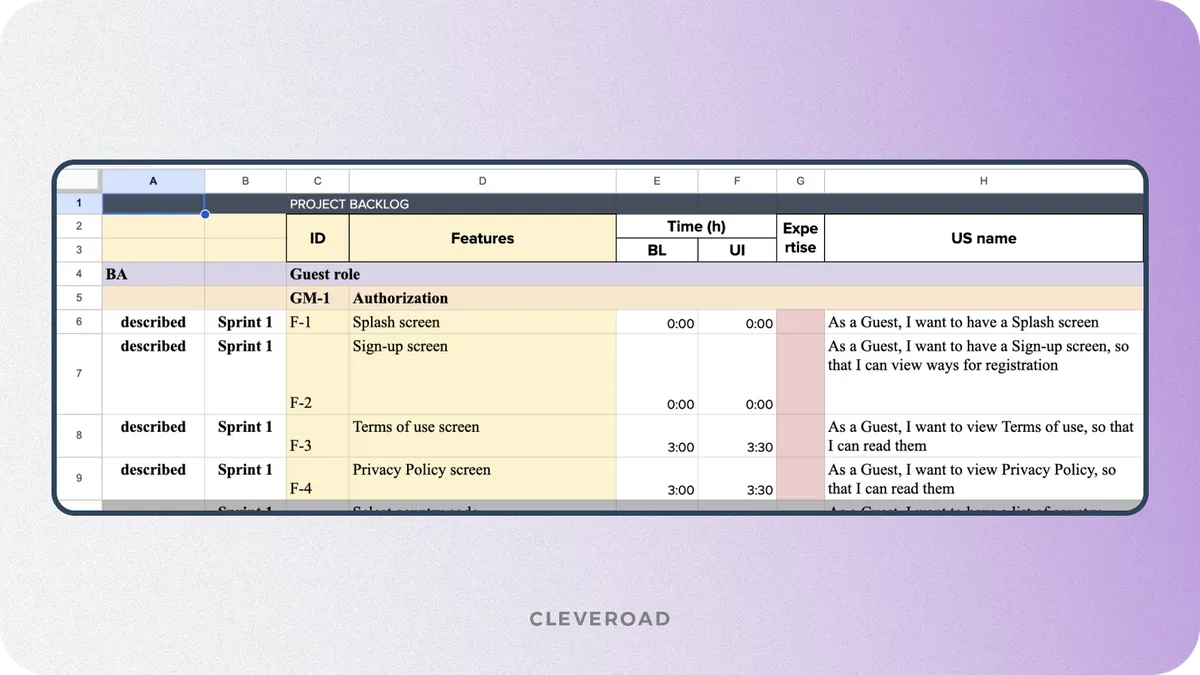
The example of product backlog for Agile in SDLC
5. Plan the sprint (iteration)
Arrange a meeting with the entire developers’ team and review all the functional elements, features, stories, and bugs in your backlog. Together, you should decide which ones are more significant to fulfill in the following project sprint.
When the tasks are properly prioritized, and the team is aware of the approximate deadlines, you are able to optimize the software Agile development life cycle completion.

Example of software development sprints planning in Agile SDLC
6. Hold daily meetings
The daily team communication allows successfully accomplishing phases of Agile model in software engineering. There are the three main questions to discuss to help the team keep up with the responsibilities fulfillment:
- What did you do yesterday?
- What are you planning to do today?
- Are there any challenges or stoppers in your tasks?
The SDLC meaning in Agile is that the completed last sprint is not the final one. Following this methodology, the software solution undergoes continuous enhancements until you reach a full-fledged version that meets all your customers' needs.
How to Make Agile the Most Effective for Your Project?
Just like with any other changes, integrating SDLC in Agile model into your project may be a challenging process. The list below indicates four basic actions to take in case you want to adopt this methodology very soon :
- Daily meetings. As it was mentioned above daily meetings are useful for leading open conversations, checking the responsibilities completion, and optimizing the workflow on each iteration.
- Live demonstrations. It means sharing the screen to display the progress of SDLC phases in Agile.
- Sharing feedback. Gather rates and reviews from stakeholders and users to analyze and negotiate them with specialists.
- Sticking to Agile. Implement alterations according to the Agile SDLC diagram and the clients’ feedback to make sure that each iteration refines the software.
- Client and IT vendor collaboration. Establish a collaborative environment between the client and the IT vendor (by using different communication tools) to ensure transparency, efficient communication, and alignment of goals throughout the Agile SDLC process.
- Task prioritization. Prioritize tasks based on their importance and impact on project goals. This ensures that the most crucial aspects are addressed promptly, enhancing overall project efficiency.
- Focus on software product quality. Emphasize the quality of the software product at every stage of the Agile SDLC model. Implement robust testing practices, code reviews, and continuous improvements to deliver a high-quality end product.
Benefits of Agile SDLC
How Can Cleveroad Help You in Agile Development?
Cleveroad is a software development company with proven in-depth experience with headquarters in Central Europe, Estonia. Our competence involves helping startups and businesses of all sizes acquire cutting-edge technologies since 2011. We specialize in ensuring a diversity of IT-related services and custom-built software solutions.
The Agile development lifecycle is our main approach, as products created with this methodology boost workflow efficiency, solve business problems, and help to gain competitive advantages.
By cooperating with us, our clients receive a row of the following benefits:
- We strongly believe that honesty with customers, partners, and teammates is a key point to building top-notch products
- Our SDLC maximally complies with the principles of Agile, the realities of today, and provides customers with high-quality software in the shortest possible time
- Cleveroad offers the three flexible partnership models: dedicated team, fixed price, time & materials
- A team of high-qualified and certified QA engineers participating in the qualitative product creation for you
- Substantial experience in software development across a range of demanded domains, like FinTech, Healthcare, Logistics, Social Media, Education, Real Estate and Retail
The Agile system development life cycle model is the more efficient, the higher the professionalism level of the software development team is. The software architecture approach described in this article in the hands of experienced specialists will help create a successful and high-quality software solution. So to build a flawless and profitable product leveraging the Agile method in SDLC, you should apply to a credible vendor with proven tech expertise to get the most out of the methodology.
Develop software with Agile SDLC methodology experts
Our team has 12+ years of experience in Agile software development and is ready to help you build robust solution according to your business needs
The Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is an iterative and flexible approach to building software that involves continuous collaboration between cross-functional teams and stakeholders throughout the development process.
SDLC can be both Waterfall and Agile. Waterfall is a traditional, linear approach, while Agile is a more iterative and collaborative methodology within the broader context of SDLC.
SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) is a framework for planning, creating, testing, and delivering software. Agile principles, outlined in the Agile Manifesto, emphasize collaboration, flexibility, and customer satisfaction over rigid processes and documentation.
Agile methodology in SDLC is an adaptive approach that focuses on delivering small, incremental improvements to software in short iterations. It prioritizes flexibility, customer collaboration, and responsiveness to changing requirements.
SDLC is a broader term encompassing various methodologies for software development, including Agile. Agile is a specific iterative and collaborative approach within the SDLC, differing from traditional linear methods like Waterfall.
The Agile SDLC typically involves phases such as planning, designing, coding, testing, and continuous delivery in short iterations called sprints.

Evgeniy Altynpara is a CTO and member of the Forbes Councils�’ community of tech professionals. He is an expert in software development and technological entrepreneurship and has 10+years of experience in digital transformation consulting in Healthcare, FinTech, Supply Chain and Logistics
Give us your impressions about this article
Give us your impressions about this article