The Impact of Blockchain and Iot in Supply Chain and Logistics
Updated 28 Aug 2023
15 Min
4276 Views
In modern customer-centric reality, delighting your clients has never been more crucial for business. The global economy bar has been set high, and basic customer service is not enough to stand out from competitors.
Therefore, companies of all industries and sizes must invest in making clients happier than ever before, and customer service is always included in business processes. It consists of various activities, but all of them are joined by one goal of bringing the added value of essential services and maximizing customers’ loyalty to the brand.
In this regard, the requirements for the digital modernization of enterprises are changing. It is especially true for businesses where technical complexity intersects with the high importance of customer satisfaction. A striking example of this kind of domain is logistics. Among the most impacting trends is active integration of blockchain and Internet of Things (IoT) in the supply chain. Transformation concerning its digitization is a must not only for business expansion but also for its long-term sustainability.
In the article, we’ll outline some of the key trends of blockchain and IoT in logistics and supply chain digital transformation and practical examples of customer service improvement in these processes.
What is included in Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Blockchain
The increasing use of this technology in logistics and Supply Chain Management (SCM) is a vibrant and sustainable trend. Blockchain offers benefits that improve customer satisfaction: transparent control, security, and processes’ optimization in real-time.
Blockchain Benefits for Logistic
With proper implementation, blockchain gives a business higher trust level between shipper and consignee and significantly simplifies decision making. All parties can access all the info constantly and in real-time; every network participant operates the same data, ensuring a single point of truth.
Blockchain integration with logistics processes and SCM brings many benefits to businesses. In particular, the technology is often applied in:
- Transportation, tracking, and certification of various goods
- Business processes optimization: it can be a document flow, delivery routes, etc.
- Security enhancement (fraud reduction and genuineness verification)
- Payments providing, disputes settlement, smart contracts, etc.
Now let’s see how blockchain works in the practice of logistic and SCM.
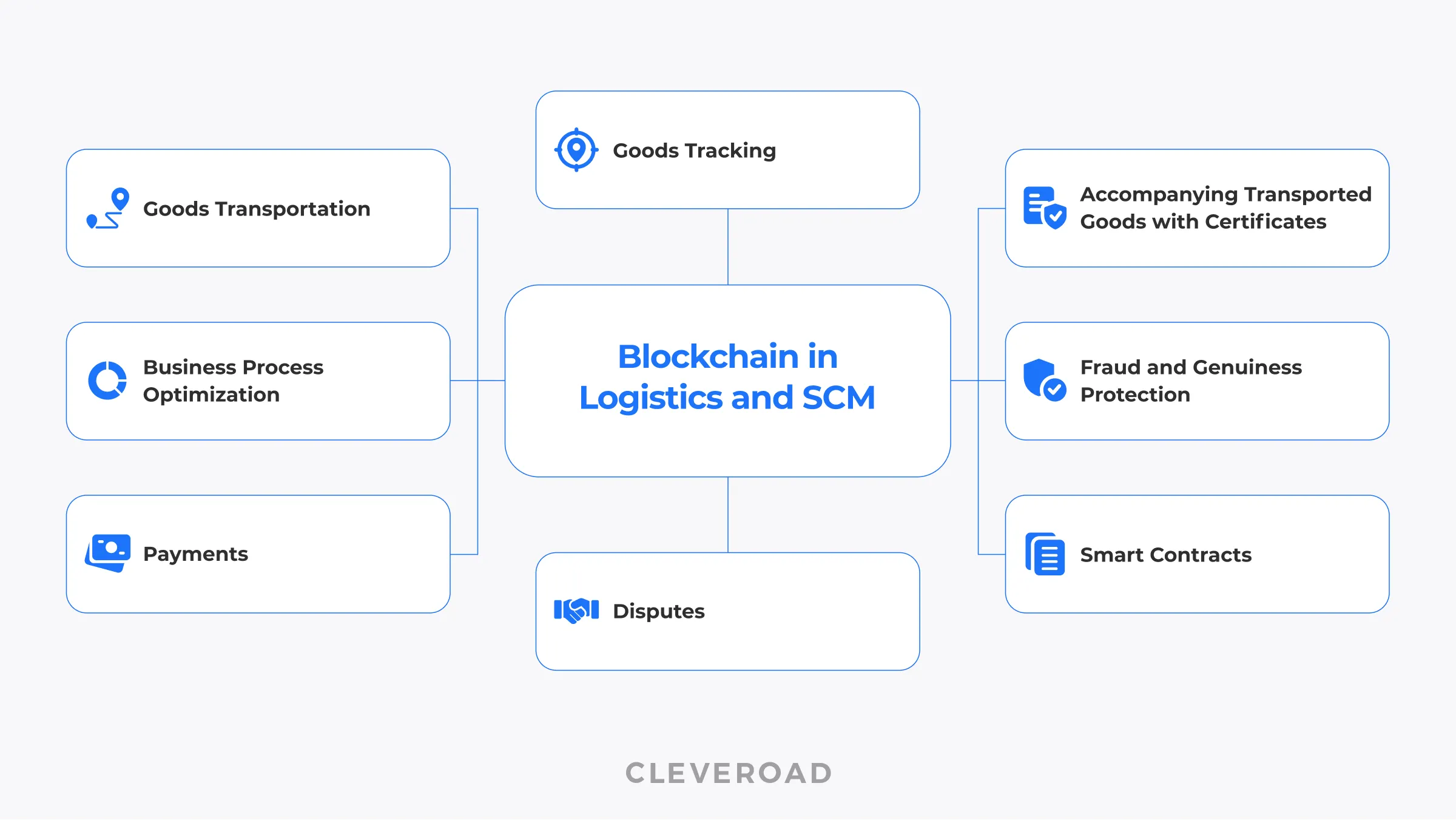
Blockchain in logistics and supply chain management
Solving Documentation Issues in Container Shipping
Resource-intensive and time-consuming document flow is an instant problem of container shipping. Massive paperwork complicates the operations of all participants. Moreover, there is a risk of fraud, loss, or tampering for Bills of Lading (BOL) and other paper freight documentation.
The problem is especially acute for international transportation. For instance, a company transporting goods in refrigerated containers from East Africa to Western Europe must obtain permits at least 30 times. The total number of interactions between people and institutions reaches 200.
The cost of trade-related paperwork processing varies from 15% to 50% of the material transport costs. And this estimate does not consider the risks of document forgery, fraud, and human-factor mistakes. But there’s a way to make document circulation and paper registers digitalization more effective.
Blockchain solutions can connect broad networks and establish robust interconnection between shipping companies, ports, and customs. IBM and Maersk proved it in their joint project:
- Blockchain was to complement legacy IT systems (instead of replacing them) and standardize the interface
- The relevant documentation and approvals were shadowed on the blockchain
- All participants of the shipping process can reach the complete data of container status through the interface
The project was successful: at the end of 2017, Maersk shadowed 15% of their container shipments on the Blockchain that is over 10 million boxes annually.
Learn how logistics software development company can help digitize your business processes
Tracking Goods Provenance
The originality and origin of goods are the subjects of an ever-growing buyers' concern. Customers are afraid of counterfeiting and want to buy ethical products. The way to satisfy these demands is to track the supply chain and documentation using blockchain technology.
The problem of counterfeiting is especially acute in the pharmaceutical industry. In addition to material damage, it threatens patients' health and even their lives — if we take, for example, drugs for cancer diseases. Blockchain can provide transparency in the supply chain from the manufacturer to the pharmacy and individual patient. With barcodes and auto-ID technology, it becomes more difficult to tamper with goods or sell counterfeit medicines.
Tracking provenance is also relevant for high-value items such as gems, luxury handbags, or watches. Certificates of origin and originality are always required, but they can get lost or tampered with. Blockchain helps to solve this serious problem. The technology greatly improves the quality of goods identification and helps to track its provenance transparently.
Blockchain allows buyers to:
- Ensure that the seller is an actual owner of the item, and the expensive thing wasn't stolen (by using publicly available records)
- Determine goods provenance: a diamond's serial number can be cut, but blockchain allows a buyer to identify a gemstone uniquely and easy
- Make ethical purchases — for instance, not support sellers of "blood diamonds" from Africa war zones or Madagascar sapphires mined with child labor exploitation
For example, Everledger startup uses blockchain to identify gemstones and records data from 40 points. It helps to uniquely identify the diamond and track its movement from owner to owner.
Control of Food Supplies
One of the biggest problems of the food supply chain is foodborne disease outbreaks. Retailers must identify points the goods came from, select items that contact dangerous food, and remove all of them from stores — really quickly.
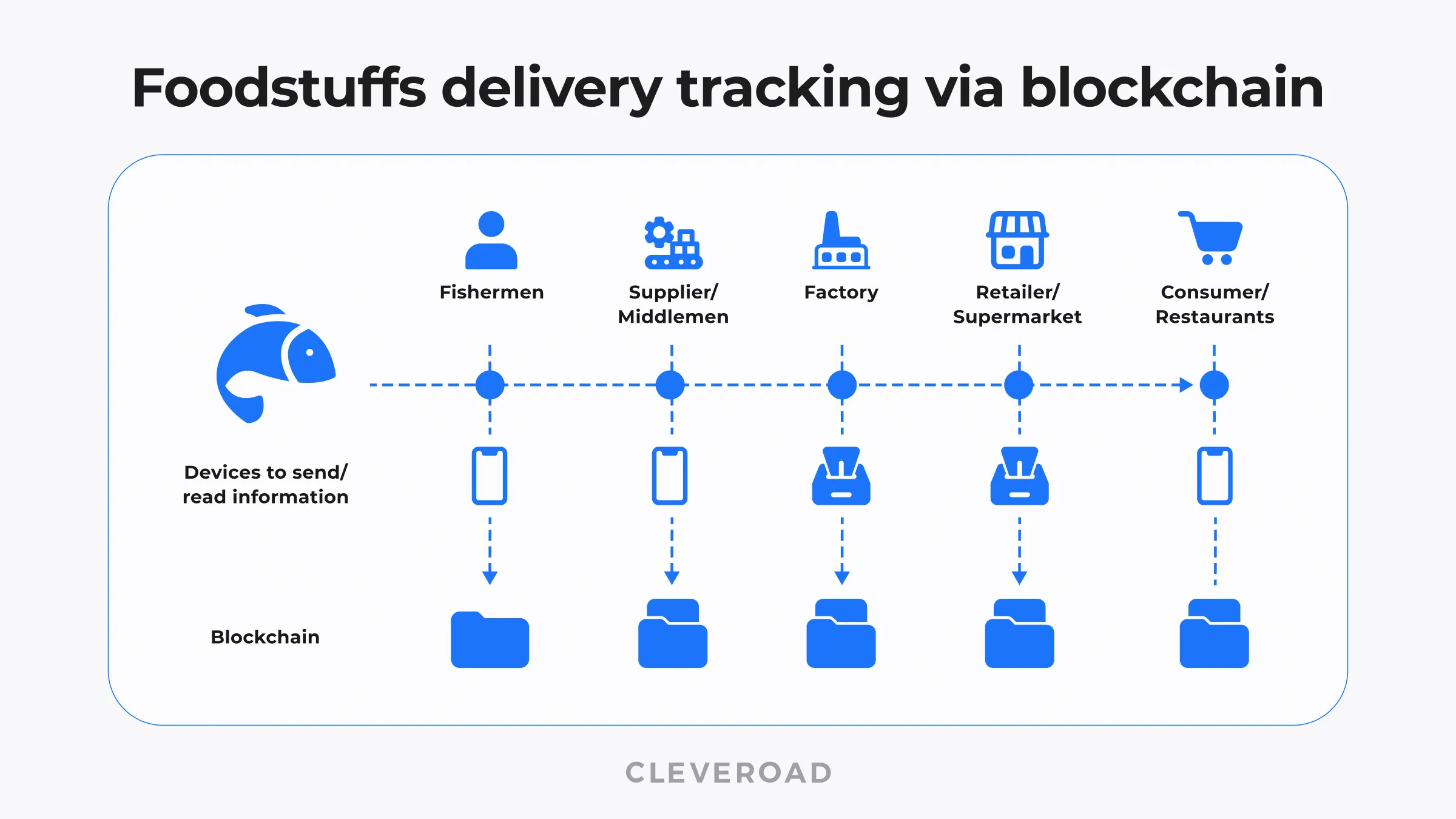
Blockchain certification and tracking at every stage of the foodstuffs supply chain
The problem is that sellers spend weeks looking for the source of the infection/contamination. In doing so, it is imperative to restore consumer confidence in the store as quickly as possible. Blockchain can resolve this contradiction and speed up supply chain tracking.
The well-known Walmart retailer uses the technology to simplify food traceability. In partnership with IBM, the company has created a blockchain-based superordinate ledger. The solution ensures the transparency of food items’ transportation and helps control the origin of goods much better than the barcodes and auto-ID technology that Walmart used before.
The superordinate ledger augments the existing IT systems used by the company's supply chain partners. Data on origin, expiration date, factory processing, delivery, and the batch number was entered into the blockchain and became available to all chain links in real-time.
Walmart has tried the approach by delivering food from local farms to small shops and internationally transporting goods from Latin America to the USA. It turned out that:
- All data became available to network participants even without a centralized database
- The infection source in a foodborne disease outbreak can be traced literally in seconds
- By using expiration dates in supply chain optimization, retailers can significantly reduce food waste
The pilots have shown the effectiveness of blockchain, and Walmart, in partnership with IBM, continues to work on such projects.
Read what are smart contracts and how they help improve and secure business processes
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things brings together physical endpoints, the data that travels from them over the network, and software. One of the most significant innovative technologies penetrates many areas, from smart homes to industrial gas pipeline management. End devices transmit data in real-time and allow the accumulation and processing of information at a low cost for the parent organization.
IoT systems use data on physical objects — in particular, transported goods. Information is transmitted via active sensor devices or passive assets such as shipping containers (connecting to electronics and the IoT Edge Devices). The IoT supply chain solutions cover a wide range of business processes and help improve them. Besides, business intelligence for supply chain allows to substantially expand the IoT opportunities.
Want to digitize your business?
Get a custom software solution to optimize processes in the logistics and supply chain
How the Internet of Things is Used in Logistics and SCM
The Internet of Things and supply chain management are increasingly referred to in a single context. The convenience and capabilities of the technology for the SCM have made it one of the most striking trends in logistics. Let’s consider how the Internet of Things impacts supply chains:
Simplify interactions over the network
The Internet of Things helps to establish data exchange over all parties. Information is transmitted securely, in real-time. IoT in supply chain allows companies to optimize decision-making management and freight transportation control.
Manage delivery with less human intervention
Smart containers with environmental sensors monitor and regulate the temperature, lighting, and humidity in the boxes. The technology ensures the safety of "sensitive" goods, helps to track containers’ location, doors opening and closing, etc.
Monitor freight units/vehicles effectively
Data from smart supply chain IoT sensors connected to digital trucking solutions (such as, freight management software, freight rate management system, etc.) allows owners to identify vehicles’ location, condition, fuel consumption, etc. Logistics companies can transparently control transportations along the route, optimize freight costs, prevent and suppress fraud, and improve fleet management.
Prevent vehicles’ breakdowns and money loss
IoT helps to implement predictive maintenance and Condition Based Maintenance (CBM) instead of scheduled inspections. By analyzing truck performance, companies predict patterns related to typical truck breakdown, gain alerts about probable malfunctions, and identify defects before they become critical.
Leverage vast data amounts for various purposes
Non-volatile sensors, combined with connectivity devices, routers, and gateways, transfer information via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or 4G and IoT-related protocols. Data is sent to the cloud and converted for calculating statistics and trends, warning of deviations and failures, etc.
Manage all transportation remotely
IoT supply chain data is transmitted to any point (the dispatch center, mobile device of the company owner, etc.). It helps reduce waiting times, respond to deviations dynamically, and optimize processes in real-time.
Let’s consider several examples of IoT in supply chain management and logistics.
Optimization of Fleet Management
The Internet of Things can power fleets in various ways, collecting data from vehicles and transmitting it to dispatch or analytic centers. End devices can pick the information about engine condition, tire pressure, fuel's level and consumption, vehicle location and speed, and driver's behavior on the route. Collected data stores and analyses to:
- Timely identify faults
- Determine the car location on the road
- Detect facts of fuel fraud, dangerous driving, or theft of vehicles

How IoT helps to optimize fleet management
Let’s illustrate how sensors work using IoT in supply chain examples of determining the driver’s behavior.
In the USA, commercial motor carriers must install the Electronic Logging Device (ELD) on every track. These devices communicate with a car’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) and receive data from the engine, brakes, and transmission. It allows ELD to collect information about drivers’ service hours and determine two core indicators — idle time and harsh events. By seeing them, the company can:
- Determine the driving aggressiveness level and degree of route difficulty using data from ELDs, gyroscopes, or accelerometers. They detect harsh turning, braking, or collisions, giving the company ability to warn employees about dangerous roads and encourage safe driving.
- Incentivize the more effective drivers and solve the idling issues (for instance, by investing in alternative technical options). Such analytics can help spend less time idling, reduce the cost of unproductive time on the road and optimize the loading of the vehicle fleet.
- Improve safety and efficiency by recording a variety of data from vehicles. For example, aggregated information from GPS trackers and sensors installed in the truck’s fuel tank, on the engine, tires, etc., helps determine why one car spends more fuel than another (the same and following the same route).
Interested in other Internet of Things capabilities? Read how IoT can be implemented in healthcare
Route Management Improvement
IoT solutions for location and route management are well-known and widely used. Truck beacons and GPS tracking systems help track vehicle location along the route, ensure timely cargo delivery, and notify customers of their orders’ progress.
In addition, IoT devices are often used in real-time warning systems. They warn dispatchers and drivers about obstacles on the road (landslides, fallen trees), accidents, helping to respond to emergencies quickly.
The Internet of Things is becoming an indispensable assistant for logistics managers in planning and controlling shipment and delivery schedules. The technology helps to instantly identify time delays, streamline business processes, and increase customer satisfaction.
Let's illustrate how GPS tracking works:
- The tracking devices are installed into a vehicle, gather various data (e.g., speed, idle time, current and historical location, unauthorized use, hours worked), and store it.
- A device determines a vehicle location in real-time using the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and transmits data via the wireless or cellular network.
- Data is transmitted to a server that acts as the cloud. It allows company managers or dispatchers to access the info via a desktop computer or mobile device.
- The supply chain IoT data is shown on a map in near real-time, allowing managers to make decisions flexibly, respond quickly to emergencies, and improve customer service.
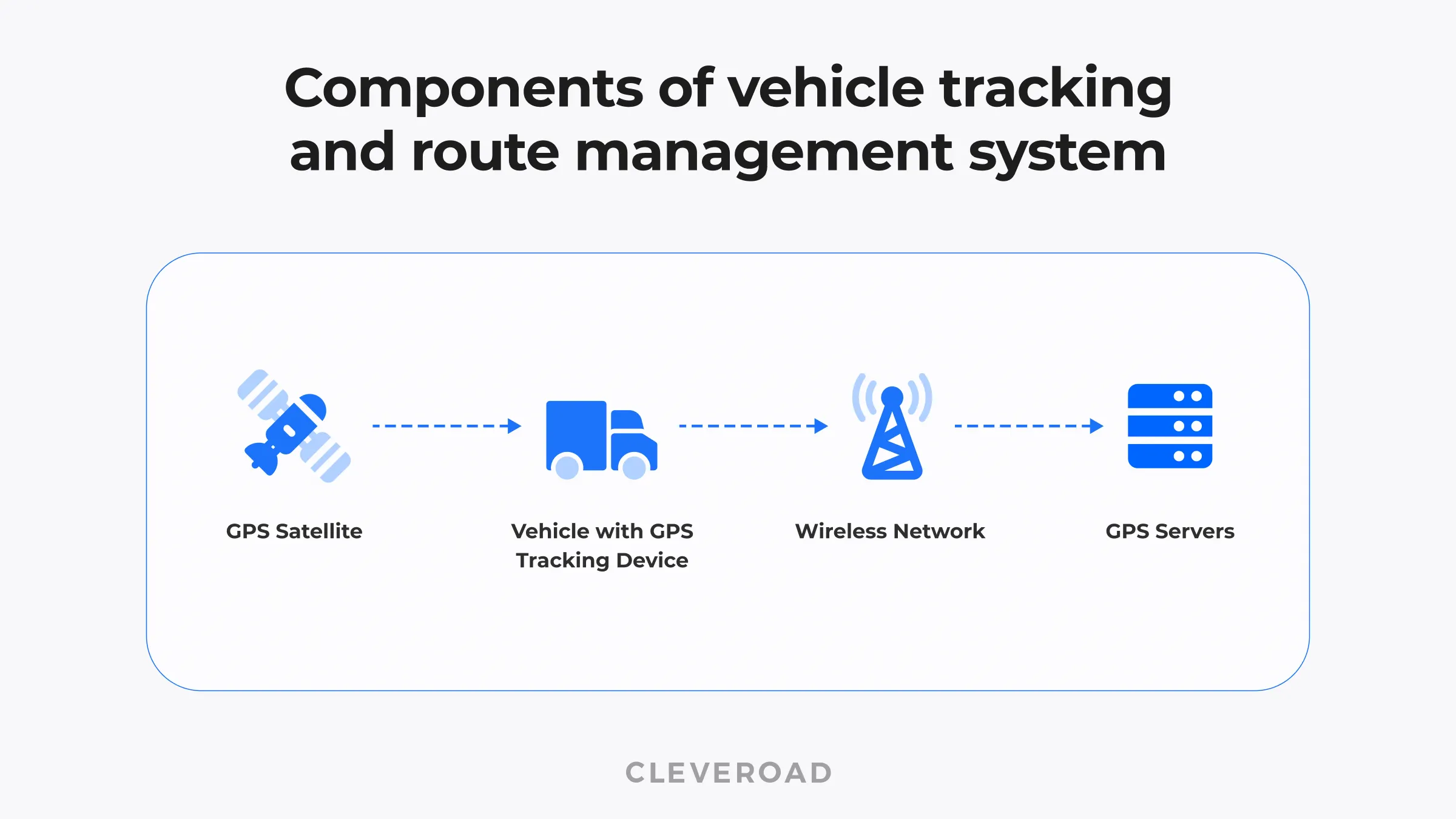
Let's see what the vehicle tracking and route control system consists of
Reduced Fuel Consumption
An IoT-based fuel control as a part of a fleet management system helps reduce the company's average fuel bill by at least 10%. The economy can be achieved with the use of fuel sensors installed in a fuel tank. They can track fuel level, consumption (per period and average), the dates and locations of refills, the drainage volumes, etc.
Combined with the Engine Control Module (ECM), GPS trackers, and analytical software, they collect essential information that helps solve various logistic and fleet management problems. Among them are:
Reducing excessive fuel consumption
Companies can eliminate “invisible” and unnoticed leaks, track internal/external fraud and siphoning, and determine fuel theft by assigning fuel cards to a truck or driver.
Transparent management of fuel cost
Employees can calculate fuel consumption for a vehicle/route to optimize costs, use custom supply chain API connections between telematic and billing systems to simplify accounting, etc.
Avoiding complex fuel reporting
The system determines fuel consumption and refills, alerts managers about any unforeseen losses, collects data for reporting, and improves driver behavior analytics.
A vivid example of the use of IoT devices is the prevention of skimming and theft of fuel cards. GPS tracking of an ELD helps detect stolen card data and warn drivers and managers of card usage in new and suspicious locations.
Real-time telematics devices also detect fuel siphoning to outside vehicles or containers. It can be a fuel level sensor or a CAN bus. Unlike ELDs, they allow managers to identify when or who drained the fuel.
IoT-Based Frameworks in Supply Chain Management
IoT has transformed the traditional supply chain into a smart one. Its beneficial effect is especially noticeable in complex and critical areas such as healthcare logistics. One of the most illustrative supply chain IoT use cases is the delivery of donated blood.
In healthcare, there are vast interactions between software, humans (medical staff and patients), processes, and service operation. All participants need to obtain real-time data to support decision-making for care deliveries. So, the healthcare supply chain and IoT networks are quite challenging to manage.
The IoT-based framework systematizes and simplifies these interactions. Applied to the blood supply chain management, technology can solve logistics issues, improve operational decision making — and save someone's life.
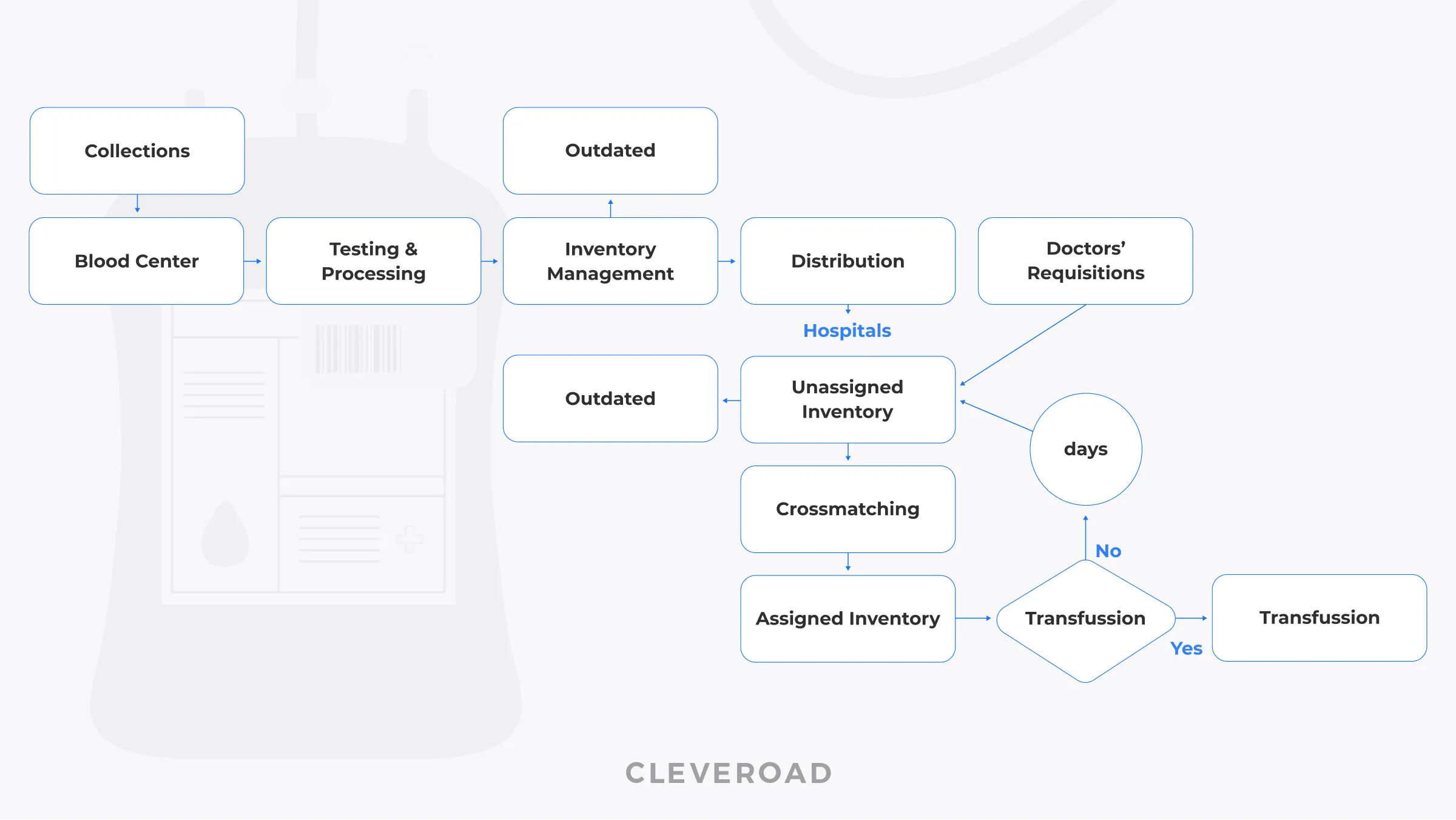
How the delivery of donor blood is organized in the IoT-based system
The IoT-based blood supply chain uses endpoints like RFID and barcodes on blood bags. Each of them connects to the whole inventory system and transmits real-time data to Blood Center and hospitals. The IoT-based supply chain management improves the performance of whole logistics process:
Blood collection and processing
Whole blood is collected at the main center, RFID or barcodes are applied to the bags, and transmit basic information (group, time of collection, etc.). This allows for more efficient management of blood transactions and stochastic supply-demand data and reduces uncertainties in the supply chain.
Donated blood distribution
The data is transferred to centers for processing whole blood into blood products, from where the packages are distributed to hospitals. IoT solutions eliminate the problem of obsolete indicators and blood shortages, maximize the use of incoming blood, and reduce unused residues.
Blood transportation
IoT sensors can track blood temperature in real-time. This control during transportation is vital for ensuring the quality and safety of blood products. The integration of the RFID system and the location tracking devices can also inform about routes where the temperature regime can be violated and harmful to blood quality.
Blood inventory management
Each blood bag connects to the inventory system via RFID and barcode. It allows hospitals to manage real-time data and stock levels, better plan blood components production, and track the actual demand. Due to the IoT network, hospitals reduce the blood outdated rate and operational costs.
Donated blood utilization
IoT systems allow tracing for blood expiration dates and storing records to minimize the number of expired units. Automatic data collection simplifies the blood authentication and ensures the adherence to transfusion standards. Moreover, IoT sensors can also monitor patients during postoperative blood transfusion.
Want to know all about the Internet of Things for business? Read our detailed IoT in business guide
Integration of IoT and Blockchain
We have considered examples of the Internet of Things and blockchain in logistics, but it should be noted that these technologies are often combined. It is understandable: data from IoT end devices must be quickly processed and transmitted, and participants need to ensure information safety at every stage. Blockchain is an excellent solution to such a problem that has been proven by many IoT use cases in supply chain.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) allows distributed and secure data storing and ensures the “immutable memory.” All participants can’t change information after it has been kept — for instance, to prove the complete task’s fulfillment to their advantage. DLT helps establish legal certainty and control crucial characteristics of goods during transportation and storage (temperature, humidity, etc.).
Consistency of data is essential for all links in the Internet of Things supply chain, and sensors and other IoT endpoints are now installed at almost every logistics facility, transmitting data to control centers. Blockchain-based solutions perfectly cope with the problem of processing and transferring vast amounts of information. They allow logistic companies to:
Connect and manage IoT devices quickly
Data can be received from various points, from trucks and containers to last-mile delivery drones (Walmart was awarded a patent for connecting them to the Blockchain).
Pay duties and fees using smart contracts
Companies can integrate blockchain into IoT devices to operate with digital currency and autonomously interact with third-party institutions (for example, pay for priority access to restricted air corridors).
Maximize the transparency of supply chain
Digital BOL and other smart contract solutions created by the integration of blockchain and IoT allow tracking goods and their characteristics at all delivery stages in real-time and ensuring accurate fulfillment of obligations.
Minimize risk of data theft and hacker attacks
Information is securely stored on the blockchain, inaccessible to attackers, but open to all parties to the agreement. Using it combined with IoT, companies can conduct transactions, terminate contracts, and control specifications.
Wrapping Up
Logistics is one of the industries where the influence of innovation trends is great and growing every day. Modernizing legacy systems and introducing blockchain and IoT requires resources, but it can turn all processes in the supply chain and make them reliable and transparent like never before. And most importantly, digitalization directly affects customer satisfaction.
Company end clients and processes participants can control the movement of goods, and delivery becomes fast and timely. Therefore, digitalization via blockchain and IoT in supply chain and logistics is a win-win strategy that maximizes both operating profit and overall business value.
Need new breath for your business?
Discover the capabilities of blockchain and IoT with full-cycle development from industry experts!
The technology is often applied in:
- Transportation, tracking, and certification of various goods
- Business processes optimization: it can be a document flow, delivery routes, etc.
- Security enhancement (fraud reduction and genuineness verification)
- Payments providing, disputes settlement, smart contracts, etc.
The Internet of Things can power fleets in various ways, collecting data from vehicles and transmitting it to dispatch or analytic centers. End devices can pick the information about engine condition, tire pressure, fuel's level and consumption, vehicle location and speed, and driver's behavior on the route.
Blockchain-based solutions perfectly cope with the problem of processing and transferring vast amounts of information generated by IoT endpoints. This combination allow logistic business to:
- Connect and manage IoT devices quickly and reliably
- Pay duties and fees using smart contracts
- Maximize supply chain transparency
- Minimize the risk of data theft and hacker attacks

Evgeniy Altynpara is a CTO and member of the Forbes Councils’ community of tech professionals. He is an expert in software development and technological entrepreneurship and has 10+years of experience in digital transformation consulting in Healthcare, FinTech, Supply Chain and Logistics
Give us your impressions about this article
Give us your impressions about this article