Machine Learning Use Cases in Supply Chain
14 Dec 2025
17 Min
124 Views
Let’s say your warehouse will know what products will fly off the shelves next week, delivery trucks dodge traffic before it even forms, and suppliers’ hiccups are flagged before they become headaches. That’s what may happen during the integration of machine learning for supply chain management. This approach will help you work smarter, cut waste, and keep customers happy.
We at Cleveroad have 15+ years of experience assisting logistics businesses in implementing tech-savvy solutions, including ML-based models. In this guide, we’ll use our own expertise to help you discover key machine learning in supply chain use cases, define how ML is integrated, and figure out costs and potential challenges to look out for.
Here’s a brief overview of the key machine learning use cases in supply chain:
- Demand forecasting and inventory optimization: ML predicts which products will be hot or not, so shelves stay stocked without piling up unsellable inventory.
- Predictive analytics and risk prediction: ML identifies risks, supplier delays, equipment issues, and sudden demand spikes, before they become expensive surprises.
- Warehouse automation and quality control: Robots and smart cameras powered by ML accelerate picking, packing, and inspection, reducing errors and frustration.
- Route optimization and logistics planning: ML finds the fastest, cheapest routes, keeping deliveries on time and fuel bills down.
- Supplier risk evaluation and performance monitoring: ML tracks supplier reliability so you can address issues early or switch partners before they impact operations.
- Supply chain visibility and intelligent control towers: ML models turn scattered data into clear dashboards, enabling you to see the whole chain and respond in real time.
- Automated master data management: ML tidies up messy product and supplier records so all systems speak the same language.
What is Machine Learning in the Supply Chain and How It Works
Machine learning (ML) is a branch of AI (Artificial Intelligence) that enables software systems to learn from data, spot specific patterns, and make predictions with no explicit programming. To minimize manual impact, ML models continuously improve as they process more information.
In logistics, supply chain, and manufacturing environments, machine learning for supply chain management helps companies address uncertainties such as fluctuating demand, transportation delays, supplier variability, and inventory imbalances. ML works by collecting data from all available systems (e.g., ERP, WMS, TMS, IoT sensors, telematics, sales channels) and analyzing it to forecast needs, optimize resources, and automate routine decisions.
The result is a supply chain that responds faster, plans more effectively, and operates with fewer manual errors. Companies benefit from real-time visibility, cost reductions, improved forecasting, and more informed decision-making across the entire network.
How ML models analyze and optimize supply chain data
Machine learning models break down complex operational data, draw meaningful insights, and help logistics teams make faster, more confident decisions. Here’s how this process typically works:
Here’s the brief overview of how ML for supply chain works:
- Data collection and integration: Pulls fragmented data from systems like ERP, WMS, TMS, IoT devices, and telematics into one unified analytical layer.
- Data cleaning engineering: Removes inaccuracies, enriches raw inputs, and prepares refined datasets that allow models to detect meaningful patterns.
- Model training: Algorithms such as Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, Neural Networks, and K-Means learn from historical operations to predict future outcomes.
- Prediction scenario modeling: Models run simulations and forecasts using time-series algorithms like ARIMA, Prophet, and LSTM to support proactive planning.
- Decision automation: Insights trigger automated actions, like reordering inventory, adjusting routes or sending alerts about potential disruptions.
Key Use Cases of Machine Learning in Supply Chain Management
Machine learning use cases in supply chain include a lot of intelligent ways to enhance workflows, reduce costs, and increase responsiveness within your logistics business. Below, we’ll explain how you can apply ML and disclose the benefits real-world businesses and companies have achieved.
Demand forecasting and inventory optimization
ML predicts future demand by analyzing historical sales, seasonal trends, promotions, and external factors. This enables businesses to optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize overstock, improving operational efficiency.
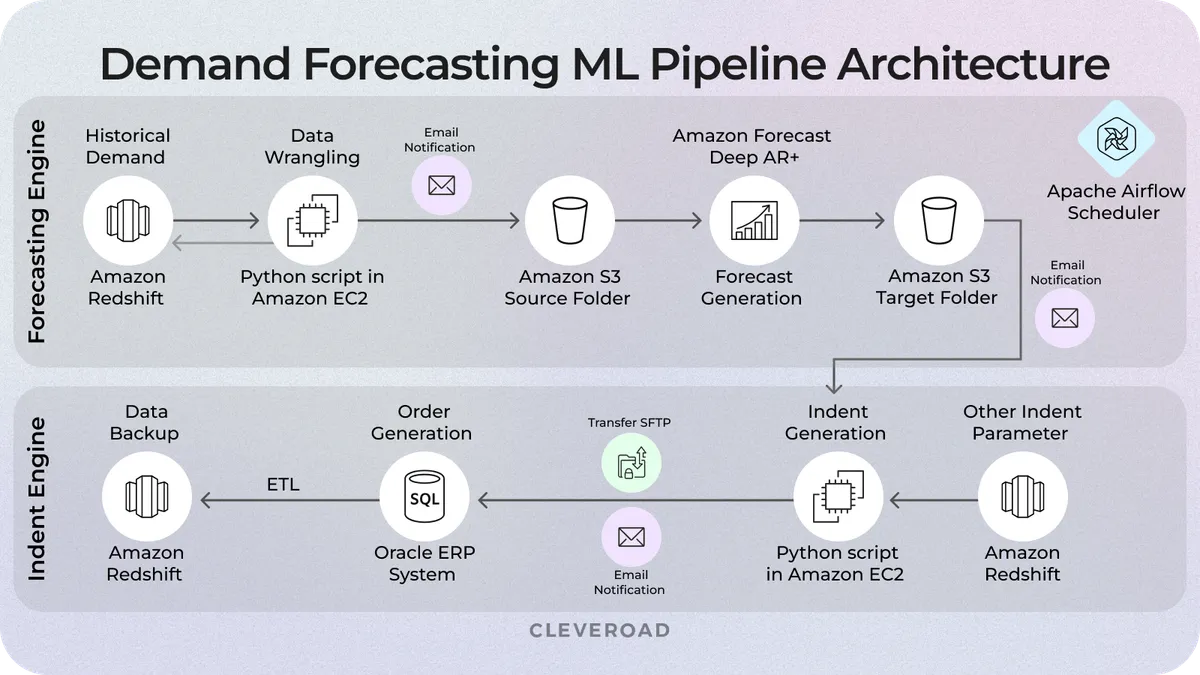
Demand forecasting machine learning pipeline architecture
Real-world example: Zara uses ML to forecast fashion demand for its stores worldwide. By analyzing sales data, regional trends, and social media signals, Zara adjusts inventory in real-time. This approach helps the retailer minimize overstock of unpopular items, reduce markdowns, and ensure popular products are available in the right stores at the right time. This is one of the most cited machine learning in supply chain use cases, as it allows rapid response to emerging fashion trends.
Predictive analytics and risk prediction
Machine Learning helps anticipate potential disruptions in the supply chain, including supplier delays, equipment failures, or sudden demand spikes. Companies can take preemptive actions to reduce risk and maintain smooth operations.
Real-world example: Coca-Cola uses ML-powered predictive analytics to monitor its bottling and distribution network. By analyzing supplier performance, weather patterns, and equipment health, Coca-Cola can predict possible delays or failures in production and distribution. This enables proactive rerouting of shipments or adjusting production schedules, reducing downtime and ensuring continuous product availability to retailers worldwide, demonstrating a strong example of supply chain management machine learning in action.
Warehouse automation and quality control
ML, often combined with robotics and computer vision, optimizes warehouse operations such as storage, picking, packing, and inspection. This reduces errors, speeds up warehouse management, and lowers labor costs.
Real-world example: Alibaba integrates ML-driven robots and computer vision in its fulfillment centers. Robots handle the transportation of goods between shelves and packing stations, while computer vision systems verify item quality and accuracy. This combination has dramatically increased throughput, reduced picking errors, and allowed Alibaba to process millions of orders efficiently during peak shopping events. This is a clear ML supply chain use case improving warehouse efficiency.
We provide a wide range of logistics software development services. Learn more about how we can help you seamlessly integate ML within your supply chain workflows
Route optimization and logistics planning
ML analyzes traffic, weather, delivery volumes, and fleet availability to plan the most efficient delivery routes. This reduces transportation costs, fuel consumption, and delivery times while improving customer satisfaction.
Real-world example: UPS uses its ORION system powered by ML to optimize delivery routes for its fleet. ORION analyzes millions of data points, including package locations, traffic, and delivery constraints. As a result, UPS saves fuel, reduces emissions, and improves delivery speed, ensuring drivers follow the most efficient routes. This is one of the most well-known machine learning use cases in supply chain for logistics optimization.
Supplier risk evaluation and performance monitoring
ML evaluates suppliers’ reliabilityusing historical delivery data, quality metrics, and external indicators. Companies can proactively identify high-risk suppliers and reduce supply chain disruptions.
Real-world example: Unilever uses ML to monitor and assess its global network of suppliers. By analyzing delivery times, quality issues, and external news about suppliers, the company can identify potential risks early. This allows Unilever to take corrective action, such as switching to more reliable suppliers, ensuring continuous product availability and maintaining reputation. This represents a strong machine learning supply chain use case for risk management.
Supply chain visibility and intelligent control towers
ML aggregates data from warehouses, transportation, suppliers, and inventory systems into unified dashboards, or “control towers.” These systems provide real-time insights, detect anomalies, forecast issues, and recommend corrective actions.
Real-world example: PepsiCo implemented an AI-powered control tower to monitor its supply chain. The system collects data from suppliers, production plants, warehouses, and logistics partners. By visualizing this information in real time, PepsiCo can quickly identify potential bottlenecks, adjust shipments, and optimize production schedules.
Automated master data management
ML automates the cleaning, deduplication, and normalization of product, supplier, and shipment data. High-quality, consistent, and well-maintained master data ensures accurate forecasting, efficient planning, and reliable reporting across all supply chain processes.
Real-world example: Target uses ML-driven master data management to maintain consistent and accurate product and supplier information across its network of stores and warehouses. By automatically identifying duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing records, Target ensures that all inventory systems have reliable data. This prevents mistakes in ordering, supports accurate demand forecasting, and is a prime example of machine learning supply chain use case in data management.
Learn more about ML development services we provide at Cleveroad, and how you can use them to satisfy the needs of your logistics business
5 Steps to Adopt Machine Learning for Supply Chain Projects
Adopting machine learning for supply chain requires a structured, end-to-end approach that combines business strategy and robust tech expertise. As an IT vendor with 15+ years of software delivery experience, we’ll help you define the essential steps to implement ML models in your logistics environment, ensuring the solution is practical, technically sound, and aligned with business objectives.
1. Define your custom ML use cases
The first step is to identify where machine learning can deliver real value in your supply chain. Keep in mind that not every process requires ML: focus on high-impact areas such as demand forecasting, inventory optimization, predictive maintenance, route planning, or supplier risk management.
Our team is closely engaged at this stage, conducting workshops with you to understand your business objectives, key pain points, and desired KPIs. We map potential supply chain and machine learning use cases and evaluate them for feasibility, considering available data and expected impact.
Defending out relevant ML use case involves a kind of structured exploration: which supply chain challenges can be solved more accurately, faster, or more cost-effectively with machine learning? The outcome of this phase is a tailored roadmap that prioritizes ML initiatives based on complexity, expected ROI, and alignment with business strategy.
Try out our AI strategy advisor to define the exact ML supply chain use case that will precisely match your business needs
2. Conduct discovery and data assessment
Once the use cases are defined, the next stage is examining the data that will feed the machine learning models. We perform a detailed data audit to assess data quality, completeness, and structure, identifying gaps such as missing fields, inconsistent formats, or unreliable sources.
Also, our experts recommend approaches for data cleansing, enrichment, and aggregation to create a reliable foundation for ML. We guide you in integrating internal data sources, such as ERP or warehouse management systems, with external datasets like market trends or weather information, if relevant. At the end of this stage, you’ll have a clear understanding of which datasets are usable, which require preparation, and how data pipelines will flow into the ML solution.
To represent how it works in real-world conditions, we’d like to share our recent case with you. Betabox, a STEM education platform serving more than 500,000 students, reached out to us to create a holistic learning environment to satisfy the needs of all of their stakeholders with all essential data centralized.
We conducted two targeted discovery phases: one for the core platform and another for a new community investment marketplace. The second initiative required translating a completely new concept, without existing market analogues, into a clear product framework.
Starting from high-level ideas and early sketches, during the Discovery we developed structured user journeys, architecture diagrams, and functional requirements that accurately reflected the Betabox team’s vision. This groundwork provided the clarity needed for confident decision-making and ensured a smooth transition into development.
To learn more insights on this project, you can examine the feedback of Sean Newman Maroni, CEO at Betabox, about our collaboration:
Sean Newman Maroni, CEO at Betabox, provides feedback about collaboration with Cleveroad
3. Build and train machine learning models
In this stage, Cleveroad’s data scientists and engineers turn prepared data into actionable predictive models. Experts select algorithms suitable for the chosen ML supply chain use cases, such as regression, classification, time series forecasting, or deep learning, and design model architectures.
We begin supply chain ML project with a AI PoC to test data quality, model logic, and real impact on forecasting or operations. If the PoC proves value, we refine it and scale it into a full solution. This approach minimizes risks, speeds up adoption, and ensures the final ML system fits your real workflows.
Then, we perform feature engineering, hyperparameter tuning, and validation to maximize prediction accuracy and ensure outputs are meaningful for decision-making. Cleveroad’s business analysts are closely engaged during the ML model building to confirm that the model’s predictions are understandable and actionable. At the end, you’ll receive a robust, trained ML model capable of generating accurate forecasts, identifying risks, or optimizing logistics.
4. Integrate ML into existing systems
Integration ensures that the trained machine learning model works seamlessly with existing supply chain processes. Our team embeds the model into ERP, warehouse management, or logistics platforms, using APIs or microservices to enable real-time communication between systems.
We focus on user interfaces, such as dashboards and alerts, so predictions and recommendations remain actionable for your operational teams. This integration ensures scalability, allowing the system to handle larger datasets and evolving business requirements over time.
5. Test, deploy, and continuously improve the ML solution
Before going live, models undergo rigorous testing across simulated and production-like environments. During deployment, the ML model is often first launched in shadow mode, generating predictions without influencing real operations, so its results can be compared with existing decision flows.
Cleveroad then supports full rollout, monitoring accuracy, performance, and anomalies to ensure reliability under real-world conditions. We also handle ongoing retraining and KPI refinement so the model stays aligned with evolving supply chain dynamics.
Challenges of Implementing Machine Learning in Supply Chains
For sure, integrating machine learning models into your supply chain flow may be a bit bumpy, especially without reliable assistance. To help you sidestep common pitfalls, we’ve outlined the key challenges and the practical solutions Cleveroad typically delivers to address them.
Distorted data and integration issues
One of the biggest blockers to ML in supply chain initiatives is the inconsistent, siloed, or outdated data that most companies rely on. Inventory logs may not match ERP records, IoT sensors may generate noisy or incomplete readings, and legacy tools often store data in formats that modern systems can’t easily interpret. When the foundation is distorted, even the strongest ML models can’t produce stable or trustworthy outcomes.
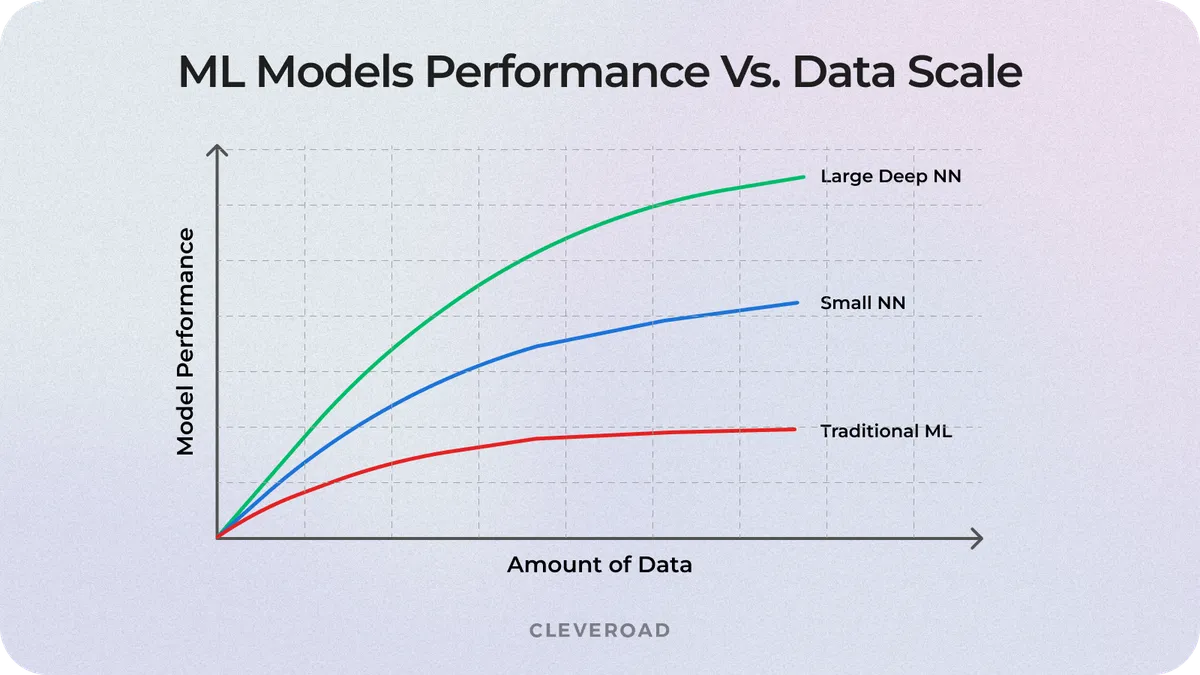
ML model performance vs. Data scale
Cleveroad’s solution: We start with an in-depth data discovery and quality assessment, mapping every data source used across operations: ERP, WMS, TMS, CRM, supplier portals, telematics, and warehouse devices. The team builds ETL pipelines and integration connectors that clean, standardize, and merge these sources into a single, structured environment. To prevent future data drift, we add automated anomaly detection, validation rules, and ongoing cleansing mechanisms, ensuring that ML models continuously receive accurate information.
High initial investment and infrastructure requirements
Implementing ML in operational environments often requires scalable storage, cloud infrastructure, GPUs, streaming pipelines, and automated monitoring. Many organizations hesitate because they fear overinvesting in systems that may not deliver instant ROI.
Cleveroad’s solution: Cleveroad reduces risk through a strategy-first approach. Instead of pushing complex architectures, the team evaluates which ML components are truly necessary for the client’s goals and which elements can be reused to avoid unnecessary costs. They design a modular and cloud-ready ecosystem that can be expanded gradually, not all at once. Clients receive a financial breakdown with projected ROI, infrastructure needs, and phased implementation so leadership can invest confidently without guesswork.
Strategy-centered approach results in a solid ML foundation that is cost-efficient, scalable, and tailored to youe real business needs, especially important if you adopt machine learning for supply chain management for the first time
Change management and workforce adoption
Even a perfectly built ML system won’t deliver value if employees don’t trust or adopt it. Teams may fear automation, struggle with unfamiliar dashboards, or continue using manual practices simply out of habit. Without proper change management, implementation slows and benefits go unrealized.
Cleveroad’s solution: At Cleveroad, we focus on implementing human-focused adoption support into every project. This includes early-stage stakeholder workshops to explain what the ML solution does, how it works, and how it benefits each team. We develop intuitive dashboards with clear predictions, alerts, and explanations that avoid the “black box” feel. Employees receive hands-on training, and the rollout happens in gradual stages, allowing users to test features, give feedback, and adjust workflows at a comfortable pace.
Cost to Integrate Machine Learning for Supply Chain
Integrating machine learning into supply chain operations typically costs from $40,000 to $350,000+, depending on project complexity, data readiness, infrastructure requirements, and the level of customization your company needs.
Below is a more detailed breakdown to help you understand what shapes the final supply chain Machine Learning budget:
- Data quality and preparation: The more fragmented or messy your existing data is, the more time engineers spend on cleaning, mapping, and integrating it.
- Complexity of machine learning use cases: A simple demand forecasting model costs far less than a full intelligent control tower or multi-model system.
- Required integrations: Connecting ML to ERPs, WMS/TMS, IoT sensors, APIs, and legacy software affects overall development time.
- Infrastructure and deployment environment: Cloud setup, GPU needs, data pipelines, and real-time processing capabilities influence both cost and timelines.
- Model accuracy and training cycles: Achieving high accuracy requires additional iterations, data labeling, and experimentation.
- Custom dashboards and UX: Tailor-made interfaces, alerts, and analytics modules add extra engineering and design work.
- Security and compliance requirements: Projects requiring advanced encryption, role-based access, SOC2 readiness, or audit trails increase complexity.
Also, based on our previous experience in machine learning integration for the logistics domain, we’ve prepared an approximate estimate for ML implementation in supply chain projects.
| Supply chain ML implementation step | Approx timeline (h) | Approx cost ($) |
Requirements analysis | 40-80 hours | $3,000-$8,000 |
Data audit, cleaning and setup | 120-300 hours | $10,000-$35,000 |
ML model development training | 200-600 hours | $18,000-$75,000 |
Integration with ERP/WMS/TMS and APIs | 150-400 hours | $15,000-$50,000 |
Building dashboards/ ML-driven features | 100-250 hours | $8,000-$30,000 |
Testing, validation and fine-tuning | 80-200 hours | $6,000-$20,000 |
Deployment | 60-50 hours | $5,000-$18,000 |
Staff training and rollout support | 20-60 hours | $2,000-$6,000 |
Keep in mind: actual values may vary based on data volume, number of use cases, and system complexity. To receive a more detailed estimate tailored to your project idea and ML supply chain use case, feel free to contact us for a custom calculation.
Cleveroad – Your Trusted Partner in Supply Chain Machine Learning Development
Cleveroad is a skilled software development vendor with deep expertise in machine learning and a strong background in supply chain, logistics, retail, manufacturing, and enterprise automation. Our team delivers end-to-end AI development services, including AI consulting, PoC creation, custom ML-based solutions for logistics, predictive modeling, and intelligent automation of operational workflows.
For more than 15 years, we’ve helped startups, mid-sized companies, and large enterprises implement ML-driven supply chain optimization strategies that enhance forecasting accuracy, reduce operational bottlenecks, cut logistics costs, and streamline warehouse and transport processes through data-powered decision-making.
When you partner with Cleveroad for supply chain and logistics machine learning initiatives, you benefit from:
- AI strategy workshop: We identify the most impactful ML supply chain use cases, define KPIs, and create a roadmap from concept to full integration
- Acceleration using ML frameworks: We use production-ready ML services like AWS SageMaker and Google Vertex AI to speed up the development of models
- Integration across your ecosystem: Our team embeds ML solutions into TMS, WMS, ERP, telematics systems, IoT sensor networks, and custom enterprise software
- AI Proof-of-Concept development: Validate ML-driven logistics automation such as predictive ETAs, risk scoring, or warehouse throughput optimization
- ISO-certified processes: ISO 9001:2015 and ISO/IEC 27001:2013 compliance guarantees quality, security, and trust across every stage of cooperation.
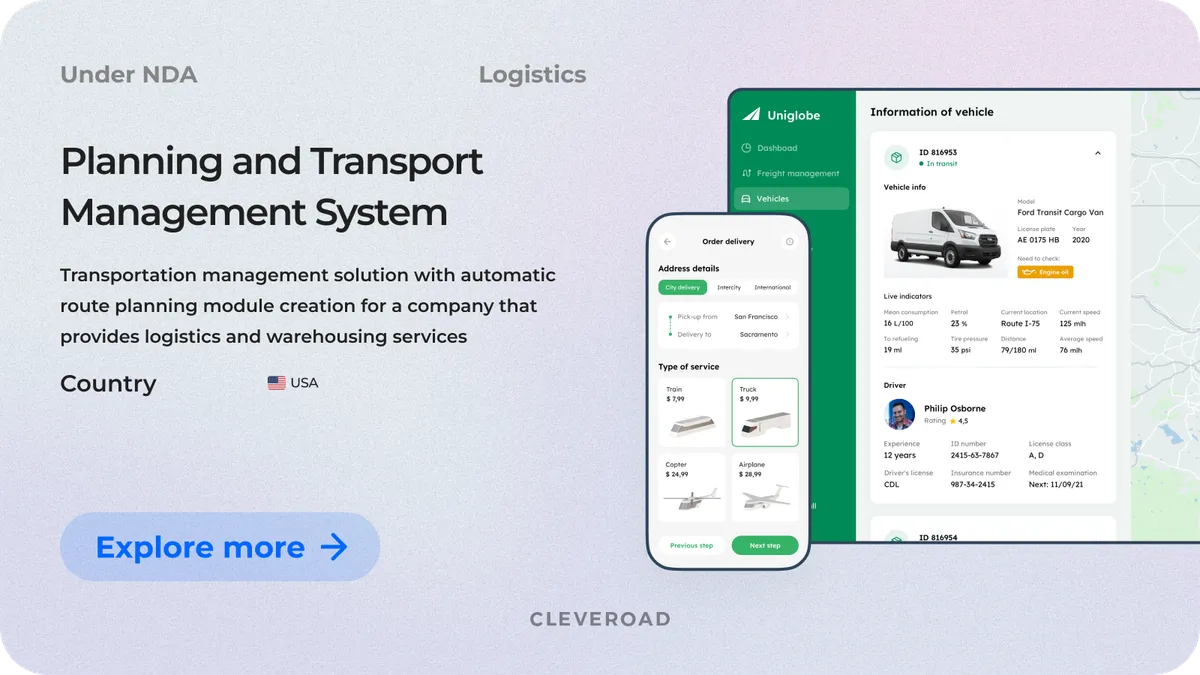
To get you familiar with our actual expertise, we’d like to show you our case – Route Planning and Transport Management System.
Our client, a U.S.-based logistics provider, reached out to us to find a scalable way to handle growing delivery volumes. Manual route planning slowed operations and created bottlenecks across the workflow. Data was scattered across systems, reducing visibility and delaying decisions.
Our experts created a flexible solution with automated route planning powered by ML models. Dispatchers gained tools for both auto-generated and manually adjustable routes. Drivers received a mobile app with custom navigation and real-time updates. The system is integrated with WMS, CRM, and warehouse processes via a new Jobs for Delivery module.
As a result, the customer received an enhanced routing system and a unified logistics management platform covering all delivery operations end-to-end. This allowed the company to streamline daily workflows, balance loads, and improve vehicle utilization across the fleet. The improved routing accuracy shortened delivery times and reduced operational losses. Ultimately, these advancements increased gross profit and strengthened overall supply chain efficiency.
Partner with Cleveroad for seamless ML integration
Our experts, proficient in creating machine learning models and deeply familiar with logistics processes and domain regulations, are ready to help you build and integrate top-notch ML model
ML, or Machine Learning, is a branch of AI (Artificial Intelligence) that enables software systems to learn from data, spot patterns, and make predictions without explicit programming. AI in supply chain leverages these capabilities to minimize manual impact, as AI models continuously improve while processing more operational data.
In logistics, manufacturing, and distribution environments, using machine learning helps companies handle uncertainties such as fluctuating demand, transportation delays, supplier variability, and inventory imbalances. Machine learning algorithms collect data from ERP systems, WMS, TMS, IoT sensors, telematics, and sales channels, then analyze it to optimize resources, automate routine decisions, and enhance supply chain planning.
Here are the key applications in supply chain where ML can make a tangible impact:
- Demand forecasting and inventory optimization: ML predicts which products will be in demand, optimizing inventory management and preventing stockouts or excess inventory.
- Predictive analytics and risk prediction: AI could anticipate supplier delays, equipment failures, or sudden demand spikes before they disrupt operations.
- Warehouse automation and quality control: ML applications like robotics and smart cameras speed up picking, packing, and inspections while reducing errors.
- Route optimization and logistics planning: Machine learning for supply chain management identifies the most cost-efficient delivery routes, lowering fuel costs and improving delivery reliability.
- Supplier risk evaluation and performance monitoring: ML continuously monitors supplier performance to flag risks early, enabling proactive procurement decisions.
- Supply chain visibility and intelligent control towers: Generating real-time dashboards, including insights from generative AI in supply chain, provides a clear visibility to respond quickly.
- Automated master data management: ML cleans and standardizes product and supplier records across all systems, ensuring data accuracy and smooth workflow integration.
Machine learning transforms supply chains by improving forecasting, optimizing inventory, and reducing both stockouts and overstock. It enhances routing, predicts risks, automates warehouse processes, and provides actionable real-time insights. By leveraging AI models and machine learning algorithms, companies can automate repetitive tasks, improve procurement decisions, enhance supply chain planning, and achieve cost savings. These innovations help businesses transform supply chains into more intelligent, responsive, and efficient networks.
To create and implement ML for supply chain, follow this steps:
- Step 1. Define your custom ML use cases. You outline where AI and machine learning will bring the most value, whether to predict demand or automate tasks across the complex supply chain. This helps map ML applications in supply chain and clarify which personalized customer or operational outcomes matter most.
- Step 2. Conduct discovery and data assessment. Teams review different types of data across the entire supply ecosystem to ensure readiness for ai and ml workflows. This stage verifies data quality for algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data effectively.
- Step 3. Build and train ML models. Engineers design models based on machine learning methods tailored to your real operational scenarios. They train machine learning and ai models to detect patterns and predict demand with growing accuracy.
- Step 4. Integrate ML into existing systems. The solution connects seamlessly with current tools using ml applications in supply chain processes. Here, AI could optimize flows by embedding machine learning algorithms directly into daily operations.
- Step 5. Test, deploy, and improve ML solution. The system is tested end-to-end, deployed, and continuously refined using ai and ml performance insights. This ensures algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data stay reliable as the entire supply environment evolves.

Evgeniy Altynpara is a CTO and member of the Forbes Councils’ community of tech professionals. He is an expert in software development and technological entrepreneurship and has 10+years of experience in digital transformation consulting in Healthcare, FinTech, Supply Chain and Logistics
Give us your impressions about this article
Give us your impressions about this article