Pharmaceutical Software Development: Complete Guide for 2026
16 Dec 2025
20 Min
143 Views
Software development in pharmaceutical industry is the backbone of operational speed, data reliability, long-term scalability, and regulatory resilience. The specialized pharma software helps you overcome industry challenges, such as:
- Inconsistent research and supply data in CMC records, cold-chain logs
- Lack of cross-team visibility between R&D, QA, manufacturing
- Manual workflows and delays in trial setup or deviation handling
- Outdated, non-compliant tools not aligned with GxP or 21 CFR Part 11
- No audit-ready traceability across lab logs, batch records, patient data, etc.
To reveal the maximum potential of the pharmacy software, you need a tech partner who understands pharma regulations and can design MedTech systems that support accuracy, transparency, and controlled data flows.
At Cleveroad, we build compliant platforms for the Healthcare industry, including pharmaceutical software. Our solutions ensure reliability under high load, audit readiness, strong data integrity, and scalability as operations grow. Based on our extensive experience, we created this guide to show how pharmaceutical software development works in 2026 and outline essential elements like system types, FDA/GxP requirements, validation processes, and the key steps required to build reliable and transparent pharma systems.
What Is Pharmaceutical Software Development?
Pharmaceutical software development is the process of creating digital tools that support critical operations in the pharmaceutical sector, covering drug discovery, clinical trials, manufacturing, regulatory workflows, quality control, and so on. If you invest in these solutions, it means you strive to improve accuracy, accelerate research and development, and reduce operational risks that delay pharma products reaching the domain market.
According to Deloitte report, 75% of organizations are increasing tech investments in data management due to rising AI and data complexity. For the pharmaceutical industry, this highlights the urgent need to modernize digital infrastructure and adopt systems that ensure data accuracy, security, and compliance.
In practice, pharma software development enables your facility to replace fragmented legacy tools, eliminate manual errors, and adopt digital systems that increase process transparency and decision-making speed. As a result, your company gains predictable, validated workflows that support both scientific progress and safe product delivery.
Major areas for pharmaceutical solutions integration
Modern software development for pharmaceutical companies supports every stage of the medicine product lifecycle, including early-stage research, clinical trials, manufacturing, regulatory operations, and market distribution.
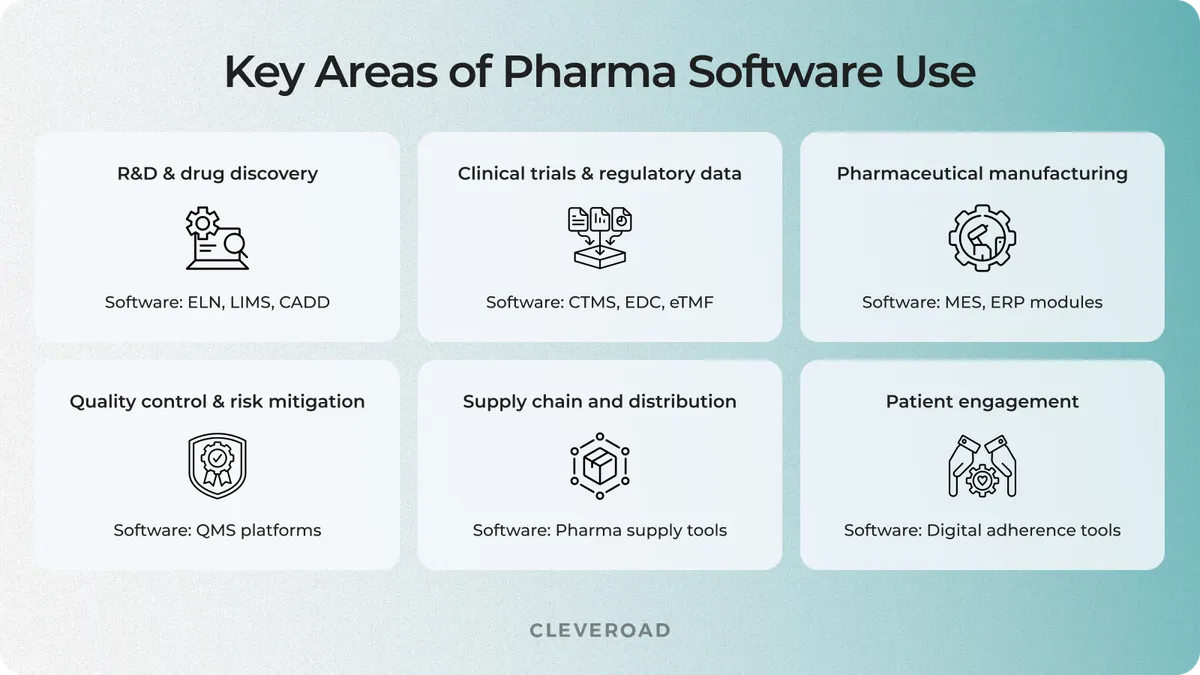
Major areas to integrate pharma software
Below are key areas where digital tools bring the most impact for biopharma purposes:
- R&D and drug discovery. At this stage, companies use tools like Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN), Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), and Computer-Aided Drug Design (CADD) platforms to manage experiments, track molecules, and organize research data with integrity.
- Clinical trials and regulatory data. Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS), Electronic Data Capture (EDC), and eTMF solutions help manage trial logistics, documentation, and patient data. Well-executed pharmaceutical software design ensures that all records in these tools meet regulatory requirements and are audit-ready.
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing and operations. Solutions like Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), ERP modules, and production analytics platforms support efficient, traceable pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
- Quality control and risk mitigation. Integrated QMS platforms enable continuous monitoring and validation during production. Software for quality control helps track deviations, automate CAPA workflows, and maintain full visibility into testing results and lab operations.
- Supply chain and distribution. Digital supply chain tools powered by IoT support inventory traceability, monitor cold-chain conditions, and prevent counterfeiting. These solutions are essential for seamless global distribution of high-value medicines.
- Patient engagement and post-market monitoring. After launch, pharma companies use digital tools to support adherence, track side effects, and gather real-world data. Such platforms provide actionable insights into how therapies perform in real-world settings, supporting both pharmacovigilance and long-term treatment success.
Bringing these systems together unlocks measurable gains in quality, transparency, and decision speed across the organization. Let’s explore the key benefits pharmaceutical companies achieve by investing in purpose-built software.
Benefits of Software Development for Pharma
Pharmaceutical software helps your company work faster, stay compliant, and eliminate manual errors across R&D, manufacturing, and quality control. Below are the key benefits you get from using custom-built solutions tailored to pharma workflows.

Key advantages of using pharma solutions
Streamlined operations and fewer manual errors
One of the biggest benefits of using a pharmaceutical software solution is the ability to reduce reliance on spreadsheets, emails, paper records, etc. Automated workflows help your teams avoid data duplication, track approvals faster, and minimize human error. The process automation is designed in software development pharma to meet strict validation and compliance standards. This design not only increases efficiency but also strengthens data reliability across departments.
Better visibility into supply and inventory
Pharma organizations often struggle with fragmented supply data and stock misalignment across regions or facilities. Integrated platforms with inventory management modules let you track batches, monitor cold-chain conditions, prevent spoilage, and avoid delays caused by out-of-stock materials.
When powered by real-time dashboards and analytics, this level of control improves both forecasting and product availability. Whether integrated into a Manufacturing Execution System or a full pharmacy management software suite, digital tools create transparency you can act on. To build on that level of visibility, pharma teams often rely on ERP systems designed specifically for regulated supply chains. Our ERP development services offer the flexibility and control needed to make that happen.
Stronger collaboration across teams and partners
Digital transformation in pharma isn’t just about compliance: it’s about enabling smarter collaboration. Modern software in the pharmaceutical industry connects R&D, QA, manufacturing, and commercial teams with shared access to critical data. Tools with integrated customer relationship management features also improve coordination with external partners, suppliers, and regulatory bodies. It eliminates silos and improves alignment across complex, multi-site operations.
Improved compliance and audit readiness
With growing regulatory complexity, staying compliant at every stage of drug development is no longer optional. Modern pharmaceutical platforms provide built-in audit trails, electronic signatures, and role-based access controls to meet standards like GxP and 21 CFR Part 11.
These features reduce audit preparation time and ensure your documentation is always inspection-ready. Compliance becomes a continuous state, but not a one-time event especially if your teams handle sensitive data and complex workflows. That's where specialized pharma development software gives you a critical advantage.
Use our Healthcare software development services to build validated, scalable, and compliant pharma solutions delivering real business impact.
Key Types of Pharmaceutical Software
To support the complex workflows of drug development, pharmaceutical companies use purpose-built software (like ELN, LIMS, CTMS, or PTMS solutions) tailored to specific operational needs. Each pharma system plays a defined role in maintaining quality, traceability, and regulatory compliance.
Below, we break down the most common types of software used across pharma workflows: each designed to solve specific challenges at different stages of product development.
Electronic Lab Notebooks
Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN) are digital platforms that help researchers document experiments, manage protocols, and store lab data in a structured, searchable format. These tools replace paper-based records and minimize data loss or inconsistency in research workflows.
Within software development for pharma, ELNs play a critical role in replacing manual lab records with traceable, compliant systems tailored to R&D workflows. These platforms improve collaboration between R&D teams and maintain consistent, validated data flows by centralizing scientific records throughout discovery cycles.
This centralization not only improves efficiency but also lays the groundwork for regulatory compliance. To meet compliance expectations, ELNs must support 21 CFR Part 11, ALCOA+, and GxP guidelines.
Killer ELN features include:
- Structured protocol templates
- Full audit trails
- Role-based access
- Real-time collaboration
- Version control and timestamped entries
Popular examples: Benchling, LabArchives, Revvity Signals Notebook
Laboratory Information Management Systems
Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) are enterprise-grade platforms designed to manage lab workflows, track samples, and store test results. These systems ensure standardization and consistency in lab operations, particularly during high-throughput testing phases. Within modern pharma software solutions, LIMS solves issues like lost samples, inconsistent test documentation, anda lack of integration between lab equipment and digital records. Strong software requirements include the ability to configure lab-specific workflows and automate reporting processes.
To meet these software requirements and ensure trust in lab outputs, LIMS must also comply with key industry standards such as GMP, GLP, ISO/IEC 17025, and ALCOA+ for data integrity.
Standout features for Laboratory Information Management Software:
- Barcode-based sample tracking
- Automated quality control rules
- Equipment calibration records
- Batch management
- Integration with ERP and ELN platforms
Popular examples: Thermo Fisher SampleManager, LabWare LIMS, STARLIMS
Clinical Trial Management Systems
Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS) are software systems that manage the planning, tracking, budgeting, and reporting of clinical trials across multiple global or regional sites. These platforms centralize study documents, schedules, subject enrollment, and site performance data. CTMS addresses key bottlenecks like protocol deviations, data silos, missed milestones, and compliance risks in complex multi-center trials.
That’s why regulatory alignment is a core requirement for any CTMS platform. Required compliance standards include ICH GCP, 21 CFR Part 11, and HIPAA if patient data is involved.
Key features of CTMS platforms:
- Site management dashboards
- Automated visit tracking
- Document versioning
- Monitoring and deviation reporting
- API integrations with EDC/eTMF systems
Popular examples: Medidata Rave CTMS, Oracle Siebel CTMS, Veeva Vault CTMS
Discover more about clinical trial software in our practical overview!
Pharmaceutical Compliance Management Solutions
Pharmaceutical Compliance Management Systems (PCMS) help pharma facilities track regulatory tasks, organize documentation, and ensure alignment with quality standards across all departments. These systems automate routine compliance workflows, streamline SOP management, and make it easier to stay audit-ready at all times.
Such tools are critical for navigating evolving regulations during drug discovery and development, where multiple teams must meet FDA expectations, GxP standards, and data integrity principles like ALCOA+. These requirements are typically addressed through frameworks such as 21 CFR Part 11, ISO 13485, and HIPAA for patient data.
Core features of PCMS systems include:
- SOP management and approval flows
- Audit trail logging
- Deviation and CAPA tracking
- Training record control
- Compliance dashboards and alerts
Popular examples: MasterControl, Veeva Quality Suite, TrackWise Digital
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software
Manufacturing software in pharma supports batch control, equipment scheduling, production analytics, and other key shop floor operations. Such platforms improve visibility into production environments and reduce errors that could lead to product recalls. Building on these core functions, the next generation of pharma manufacturing software is designed to deliver even greater traceability, integration, and automation.
The future of pharmaceutical software lies in digital manufacturing systems that ensure precision, full traceability, and seamless integration with both R&D and distribution workflows. They eliminate paperwork bottlenecks and provide real-time process control. Achieving compliant digital manufacturing requires alignment with frameworks like GMP, GAMP 5, 21 CFR Part 11, and CSV to ensure system reliability and audit readiness.
Key manufacturing software functionality:
- Batch record generation
- Digital SOP enforcement
- Nonconformance tracking
- Integration with MES, ERP, LIMS
- Validated electronic signatures and audit logs
Popular examples: Werum PAS-X, Siemens Opcenter, Emerson Syncade
Pharma Supply Chain Solutions
Pharma supply chain platforms are enterprise-grade systems that coordinate inventory control, cold-chain logistics, order orchestration, and distribution tracking to ensure compliant delivery of temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products. These platforms digitize logistics workflows, enabling automated spoilage alerts, real-time batch-level monitoring, and audit-ready documentation aligned with global shipping standards (e.g., DSCSA, EU FMD).
Modern supply chain solutions are typically cloud-based and API-driven, integrating with ERP modules, WMS, IoT sensors, and serialization systems to support real-time traceability and robust anti-counterfeit protection. They provide end-to-end data visibility and enable continuous validation across all critical nodes in the pharmaceutical distribution network.
To remain compliant across borders, such systems must align with regulations such as DSCSA, EU FMD, GxP, and ICH Q10 governing pharmaceutical quality and supply chain integrity.
Top features of pharma supply chain software:
- Temperature and location monitoring via IoT
- Automated serialization and barcode scanning
- Real-time inventory dashboards
- Supplier qualification workflows
- Alerts for chain-of-custody breaches
Popular examples: TraceLink, SAP Advanced Track and Trace, Optel Vision
Let’s summarize the key types of pharmaceutical software, their core purposes, regulatory requirements, and the features that make them essential for compliant operations.
| Pharma software types | Purpose | Regulations | Key features |
ELN | Document lab experiments digitally | 21 CFR Part 11, GxP, ALCOA+ | Audit trails, versioning, templates |
CTMS | Manage clinical trial workflows | ICH GCP, 21 CFR Part 11, HIPAA | Site tracking, deviation logs, eTMF/EDC integration |
LIMS | Track lab samples and test data | GMP, GLP, ISO 17025, ALCOA+ | Sample tracking, QC rules, ERP/ELN sync |
Compliance tools | Automate SOPs and audits | GxP, ISO 13485, HIPAA | SOP workflows, CAPA, training logs |
Manufacturing | Control production and batch processes | GMP, GAMP 5, CSV | Batch records, SOP control, MES/ERP integration |
Supply chain | Ensure delivery traceability | DSCSA, EU FMD, ICH Q10 | IoT tracking, serialization, cold-chain monitoring |
How to Develop Robust Software for Pharmaceutical Companies?
Software development in the pharmaceutical industry requires regulatory alignment, secure data flows, and domain-specific validation. Effective platforms must support the full pharma solution creation lifecycle, from research and development to manufacturing, while ensuring traceability and audit readiness.
That’s why software development for pharma works best with a tech partner who understands the risks and regulations. At Cleveroad, we build scalable, validated Healthcare systems tailored to the pharmacy sector.
Here’s how the pharmaceutical software development process works when partnering with our team.
Step 1. Solution Workshop and Discovery Phase
We begin with a Solution Workshop, a free consultation where our Solution Team (including business analysts, solution architects, designers, etc.) explores your pharmaceutical business goals, regulatory landscape, and operational challenges. This stage allows us to shape a high-level technical vision and deliverables such as architecture diagrams, feature lists, and cost estimates.
If you move forward, we transition to the Discovery Phase. Here, we:
- Analyze your R&D, clinical, or manufacturing workflows
- Define user roles, access levels, and data security rules
- Refine platform scope and non-functional requirements
- Finalize the Software Architecture Document (SAD)
- Create UX concepts and technical risk assessments
In complex pharmaceutical projects, we may split the Discovery Phase into multiple tracks: for instance, one focused on the core GxP-compliant platform, and another tailored to innovative modules such as trial optimization tools or AI-driven analytics. This approach helps mitigate risks early and ensures every component meets domain-specific expectations.
Step 2. UI/UX design for pharmaceutical software
After the tech requirements and workscope for your pharma software project are finalized, our UI/UX design services team creates detailed user flows and interface designs tailored to regulated pharma environments. These designs account for user roles, access permissions, and compliance expectations like GxP or HIPAA. We ensure the interface prevents input errors, maintains full traceability, and clearly reflects system logic across teams. After approval, the design is handed off to the development team as a complete, structured foundation.
Step 3. Pharmaceutical software development and testing
Based on the approved UI/UX, our engineering team begins building the platform functionality using an iterative Agile process. We develop in sprints, each covering specific features with peer-reviewed code, documentation, and validation checkpoints aligned with GxP and CSV principles. Our QA engineers test each module to ensure data integrity, security, and readiness for regulatory inspections.
If you're planning a mobile product, explore our pharma app development guide to understand how we build compliant, scalable applications for the pharmaceutical industry. Whether it’s a web-based QMS or a mobile trial companion app, we ensure your software is robust and validated.
Our clients consistently highlight the professionalism, adaptability, and deep domain expertise of Cleveroad’s healthcare software development team. They value our ability to understand complex requirements, structure ambiguous ideas into actionable plans, and deliver compliant solutions that meet industry standards.
Look at how Breanne Butler describes the cooperation with Cleveroad on QMS system creation:
Breanne Butler, Client Liaison Officer at Prime Path Medtech™
Step 4. Pharma solution launch
At this stage, we help you transition your pharmaceutical platform from test to production while ensuring full alignment with regulatory frameworks. Our team:
- Conducts Installation Qualification (IQ) to confirm proper system setup
- Configures validated staging and production environments
- Integrates your solution with essential platforms like LIMS, CTMS, QMS, or ERP
- Prepares and delivers a full documentation package, including system architecture, validation protocols, release documentation, and audit-ready credentials
This step ensures your pharma software is deployed in a compliant, traceable, and inspection-ready environment, minimizing risks during FDA, EMA, or internal audits. After launch, we provide you with a full documentation package, including system architecture details, validation protocols, configuration records, and all materials required for regulatory audits.
Step 5. Maintenance and support for long-term success
Post-release support is optional, but highly recommended for any pharmaceutical software platform, given the industry’s constant regulatory oversight and need for sustained, long-term compliance. Ongoing maintenance ensures your solution stays fully compliant with evolving domain regulations like GxP, HIPAA, and 21 CFR Part 11, remains audit-ready for regulatory inspections, and maintains strong data protection. It also ensures the software scales reliably and securely as your business grows and user or data loads increase.
By investing in software that evolves with your operations, you reduce technical debt and create room to accelerate drug development at scale. At Cleveroad, we treat post-launch support not as an add-on, but as a strategic component of delivery.
What Are the Key Regulations and Standards to Comply with for Pharma Software Development?
Regulatory compliance is not optional in pharma development software. Whether you're building research tools, clinical trial platforms, or pharmaceutical manufacturing software, the entire pharmaceutical software must align with industry-specific standards to ensure data integrity and patient safety.
It is necessary because pharmaceutical systems are designed for high-risk environments, where even a small failure in logic, traceability, or access control may have serious legal or clinical consequences. Failure to meet mandatory regulations can lead to:
- Rejected product batches or trial data
- Failed FDA or EU inspections
- Delays in go-to-market timelines
- Inability to legally use the software
- Reputational and financial damage
We’ll cover the key regulations and frameworks every pharma software solution must comply with.
FDA 21 CFR Part 11
21 CFR Part 11 is a U.S. FDA regulation that governs the use of electronic records and signatures in regulated systems. For any pharmaceutical software development involving clinical or manufacturing data, this rule ensures that digital records are secure, traceable, and legally equivalent to paper documents. It applies to systems like ELN, CTMS, LIMS, pharmaceutical ERP software, and QMS platforms used in clinical, manufacturing, and compliance workflows.
To comply with 21 CFR Part 11, software must support secure logins, role-based access, validated audit trails, electronic signature workflows, and tamper-proof recordkeeping. For any company following a guide to pharmaceutical software, Part 11 is a foundational requirement.
ALCOA+: Principles of data integrity
ALCOA+ is a framework promoted by the FDA and EMA to define how digital records should be handled to ensure trust and traceability. This framework stands for Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate: plus Complete, Consistent, Enduring, Available.
ALCOA+ principles in data management for pharma apply across R&D, QA, and clinical platforms, ensuring digital entries can be trusted during audits and inspections. ALCOA+ is embedded in most validation protocols and must be enforced at the UI/UX and database levels of pharmacy software.
HIPAA: Patient data privacy
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability (HIPAA) is a U.S. regulation that applies to any new software handling Protected Health Information (PHI). This regulation for pharma includes patient-facing apps, clinical trial tools, and digital consent platforms.
HIPAA compliance ensures:
- Encrypted data storage and transfer
- Patient identity protection
- Access logging and permissions
HIPAA is essential for companies in pharma development software when working with real-world evidence, ePRO data, or patient enrollment systems.
How to comply with HIPAA requirements? Learn more in our guide!
GxP: GMP, GLP, and GCP guidelines
GxP is a collective term covering essential quality standards in the pharmaceutical domain, including Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), and Good Clinical Practice (GCP). Each of them applies to a specific phase of the pharma lifecycle: GMP governs pharmaceutical manufacturing software, GLP covers preclinical research systems, and GCP regulates clinical trial platforms such as CTMS or eTMF. These frameworks set requirements for SOPs, traceability, record-keeping, and system validation. Non-compliance can result in rejected submissions, regulatory penalties, or revoked operational licenses.
ISO/IEC 27001: Information security
ISO/IEC 27001 is an international security standard for managing sensitive data, particularly in cloud or hybrid environments. It applies to nearly all enterprise pharma systems, including LIMS, MES, and pharmaceutical ERP software.
This standard is key for building trust in global deployments and helps ensure:
- Risk-based security policies
- Documented access controls
- Secure third-party integrations
- Structured incident response plans
Teams working on validated pharma platforms need ISO 27001 alignment as part of overall system hardening. At Cleveroad, we follow ISO/IEC 27001-aligned processes in both internal operations and client-facing software development.
GDPR: Data Protection for EU Markets
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict rules on how personal data is collected, processed, and stored within the European Union. It covers core principles such as user consent, data minimization, and the right to be forgotten. For pharma companies operating in or serving the EU, ensuring GDPR compliance is essential, especially when platforms handle patient records or study participant data.
GDPR affects clinical trial software, patient-facing apps, and marketing tools integrated with pharma development software. Even non-EU vendors must comply when working with EU-based users. In global deployments, GDPR is often implemented alongside HIPAA to ensure dual compliance for both EU and U.S. regulatory environments.
Below is a quick overview of the core regulations and standards your pharmaceutical software must comply with, along with where and how they apply.
| Regulation or standard | What it covers | Applies to |
FDA 21 CFR Part 11 (The US) | Secure digital records and electronic signatures | ELN, CTMS, LIMS, ERP, QMS |
ALCOA+ (The US, EU, globally) | Data integrity: Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate | R&D systems, clinical platforms, QA tools |
HIPAA (The US) | Privacy and security of Protected Health Information (PHI) | Patient apps, ePRO tools, clinical trial software |
GxP (Global, with variations in US, EU, and other regulated markets) | Good practices for manufacturing, lab, and clinical systems | MES, LIMS, CTMS, manufacturing platforms |
ISO/IEC 27001 (International) | Information security and risk management | Cloud-based platforms, ERP, LIMS, MES |
GDPR (European Union and any entity processing EU citizen data) | Data protection for EU citizens | EU-facing apps, clinical systems, marketing platforms |
TOP-4 Innovations Boosting Pharmaceutical Software Development
Innovation plays a critical role in developing pharmaceutical software that meets today’s demands for speed, scalability, and compliance. Technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain are no longer experimental: they’re actively used in the pharmaceutical industry to accelerate discovery, automate processes, and improve data integrity.
When working with a development partner that specializes in custom software development, pharma companies can turn these innovations into practical tools for growth.
1.AI and ML
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming how pharma companies identify drug candidates, simulate outcomes, and automate decision-making. These technologies are especially impactful in preclinical stages, where AI models accelerate molecule screening and reduce R&D timelines. ML algorithms are also used in software development in the pharmaceutical industry for risk prediction, patient stratification, and anomaly detection in clinical data.
Integrating AI into pharma platforms requires strong data pipelines and domain-specific tuning, but the results enable smarter, faster operations. As part of pharma development software, AI tools enhance precision and scalability across the lifecycle.
Explore our AI development services to accelerate drug discovery, automate analysis, and improve clinical decision-making
2. Cloud computing
The shift to cloud-based pharma software enables global collaboration, real-time data access, and scalable platforms without heavy infrastructure investments. Cloud environments support elastic workloads for modeling, clinical data processing, and batch analytics while providing built-in security controls to meet compliance requirements.
In modern pharmaceutical software architectures, cloud hosting is critical for rapid deployment, continuous integration, and disaster recovery. It also simplifies integration with third-party systems such as EDC platforms and regulatory data sources. Choosing the right cloud strategy is essential for building flexible, audit-ready pharmaceutical applications.
3. Blockchain
Blockchain technology enhances traceability and data integrity in selected pharmaceutical workflows, particularly across supply chain tracking, batch provenance, and audit logging. It enables immutable, timestamped records that support transparency and controlled data sharing in compliance-sensitive environments.
In the life sciences and pharmaceutical industry, blockchain is applied to anti-counterfeiting initiatives, cold-chain verification, and audit support processes. When integrated into new software solutions, permissioned blockchain architectures help improve trust, transparency, and data consistency without replacing validated core systems. Adoption remains strongest in distribution tracking, supply integrity, and quality assurance modules.
4. Internet of Things
IoT devices enable real-time data collection and continuous monitoring across pharmaceutical laboratories, production lines, and logistics networks. Sensors embedded in equipment or shipments continuously capture temperature, humidity, vibration, and movement data, securely feeding it into centralized software systems for analysis and alerts.
For pharmaceutical companies, IoT use translates into proactive quality control and real-time visibility into production and delivery status. IoT integration has become an increasingly standard component of pharma software development, particularly in GxP-regulated environments. As part of modern software strategies, IoT in Healthcare helps reduce product loss, improve safety, and meet audit requirements.
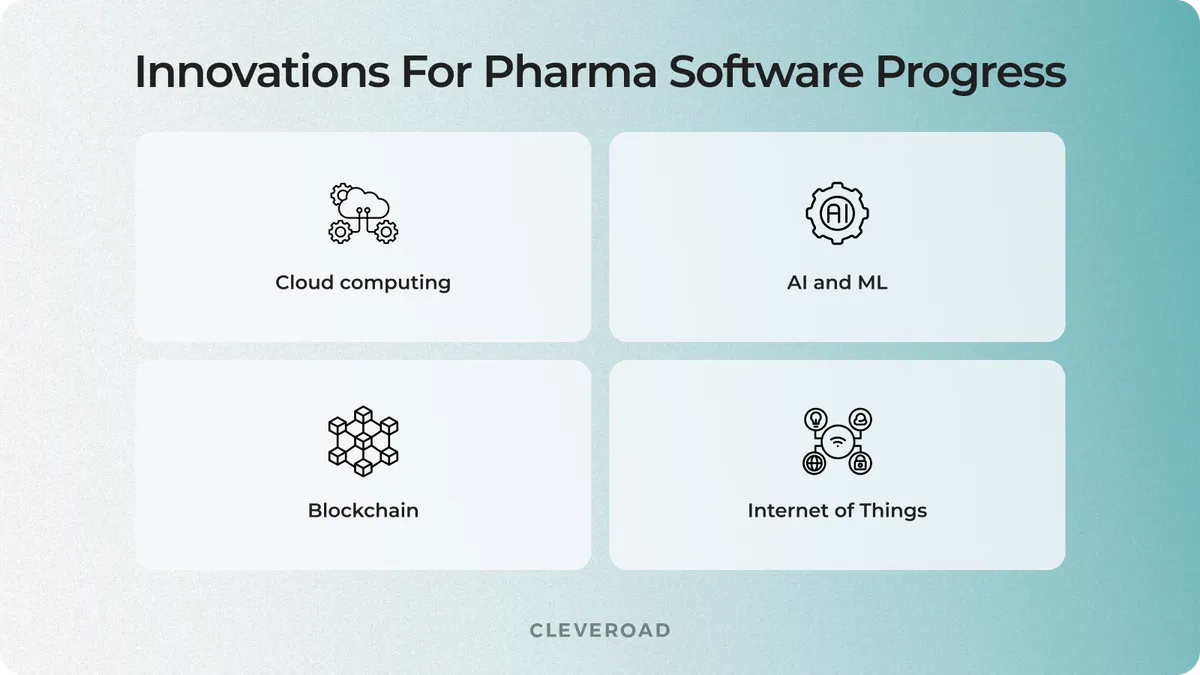
Innovations to use for pharmaceutical software development
These innovations deliver value only when applied with deep technical and domain expertise. At Cleveroad, we combine pharmaceutical software development with proven architectures to help you implement AI, cloud, IoT, and blockchain in validated, production-ready Healthcare systems.
How Much Does It Cost to Build Pharmaceutical Software?
The cost of software development for pharma depends on multiple factors: system complexity, number of user roles, compliance scope, and required integrations (e.g., LIMS, CTMS, ERP). Since most pharmaceutical platforms must meet strict validation and data protection standards, initial investment is higher than in non-regulated domains, but so are the long-term returns in speed, audit readiness, and scalability.
Here’s a rough breakdown of what typical pharma systems may cost to develop:
- R&D tools (ELN, LIMS): $80,000–$180,000+
- Clinical platforms (CTMS, eTMF): $120,000–$250,000+
- Manufacturing and MES systems: $150,000–$300,000+
- Supply chain and serialization tools: $100,000–$200,000+
- Cross-functional pharma software (QMS, audit trail engines): $90,000–$220,000+
These ranges reflect not only feature scope but also validation efforts, secure architecture, and long-term maintainability: all of them are essential when starting to create the right software for a regulated environment.
If you’re investing in software development for the first time or replacing legacy tools, Cleveroad can help optimize costs by reusing pre-validated components, offering modular delivery, and focusing only on what drives value. We design modern software solutions that fit your goals and budget without sacrificing quality or compliance.
Moreover, in case you want to optimize mobile development costs for your pharma software, Cleveroad offers Flutter app development services that reduce time-to-market for your app launch and ensure consistent compliance across devices. By using a single codebase for both iOS and Android, Flutter speeds up development cycles, simplifies testing, and allows quicker deployment of validated features, while maintaining regulatory alignment.
Why Choose Cleveroad for Pharmaceutical Software Development
Cleveroad is a Healthcare software development company with 15+ years of experience working with regulated industries. We help pharma organizations digitalize critical workflows by building solutions for R&D data management, clinical trial operations, manufacturing control, and regulatory compliance. To enhance the value of these platforms, we also integrate AI, IoT, and cloud technologies. These tools enhance traceability, automate repetitive tasks, improve cross-departmental decision-making, and accelerate validation and audit readiness.
Our portfolio includes successful projects for Healthcare, MedTech, and life science clients, including platforms with role-based access control, real-time analytics, and validation-ready architecture. We know how to work with complex pharmaceutical data, ensure alignment with standards like GxP and HIPAA, and deliver secure systems that scale with your business.
One of our recent projects involved building a Mental health app for the Nedley Depression and Anxiety Recovery Program in the US. The client needed a flexible system to manage patient data, lab results, and physician-diagnostic center collaboration. Their legacy tools lacked interoperability and failed to meet modern security and compliance requirements. Cleveroad was brought in to design a scalable, HIPAA-compliant platform from scratch.
We developed a modular web solution with role-based access, secure data exchange, and integrations via FHIR APIs. The app features include dynamic lab request forms, result dashboards, and audit-ready workflows. The platform improved diagnostic transparency, reduced turnaround times, and ensured full compliance with healthcare data standards.
This is what Neil Nedley told about our cooperation:


In this project, we worked with sensitive medical data, which required strict storage rules, secure handling, and alignment with privacy regulations. These are the same challenges faced in pharmaceutical software development, where clinical records, research outputs, and trial data must be processed predictably, securely, and at scale.
Build your pharma platform with a trusted tech partner
Partner with a healthcare software development company with 15+ years of experience to build secure, compliant, and scalable pharma platforms tailored to regulated environments
Pharmaceutical software development is the process of designing, building, and validating digital tools that support the full pharma product lifecycle. These solutions are built to meet industry-specific standards and ensure traceability, data integrity, and process automation across high-risk workflows.
Key features include audit-ready recordkeeping, role-based access, validation protocols, and seamless integration with lab, clinical, and ERP systems. Pharmaceutical software is also expected to support compliance with GxP, 21 CFR Part 11, HIPAA, and other standards, ensuring every step of the workflow is traceable and inspection-ready. In addition, such software must maintain high availability, data accuracy, and scalability to support growing volumes of sensitive information and regulatory complexity.
Here’s how we develop pharmaceutical software at Cleveroad:
- Solution Workshop and Discovery: Define goals, roles, compliance needs, and architecture.
- UI/UX design: Create GxP- and HIPAA-compliant user flows and interfaces.
- Development & testing: Build features iteratively and validate them through QA.
- Launch: Deploy to a validated environment and provide full audit-ready documentation.
- Support: Ensure ongoing compliance, scalability, and inspection readiness post-release.
The cost depends on system complexity, user roles, compliance scope, and integrations. For example, ELNs or LIMS start from $80,000+, while clinical and manufacturing platforms may range from $120,000 to $300,000+.

Evgeniy Altynpara is a CTO and member of the Forbes Councils’ community of tech professionals. He is an expert in software development and technological entrepreneurship and has 10+years of experience in digital transformation consulting in Healthcare, FinTech, Supply Chain and Logistics
Give us your impressions about this article
Give us your impressions about this article