Popular Software Development Methodologies Comparison: Full Overview
Updated 05 Sep 2023
17 Min
10159 Views
Even the smallest software development project involves a dozen IT specialists, lots of meetings, planning, discussions, and typically strict deadlines for the team to meet.
That’s why development companies apply different software development methodologies and frameworks. The most popular of them are the following:
- Agile — one of the most prominent methodologies for companies of all sizes
- Waterfall — traditional software method, linear and strict
- Lean software engineering methodology — focusing only on value-adding activities
- Feature Driven Development — combination of software development techniques aimed to produce software products as soon as possible
- Rapid Application Development — methodology concentrating on quick prototype releases and software development iterations
- DevOps software methodology — accelerating product’s time to market
They help to standardize the process, making it clear what’s going on with the product for both clients and internal teams.
In this article, we’re reviewing the most popular software development methodologies — Agile, Waterfall, Lean — and review some of their famous frameworks.
What Is Software Development Methodology?
Before going through the methodologies list, let’s define: software development methodology is a process of how to build your software. It includes a set of activities connected to planning, designing, and testing software product totally fulfilling the client’s aims.
Companies that provide software development services can build products in many different ways: moving from more to less important tasks, in alphabetical order, in order of your preference, and so on. Developers may work for just two days per week, five days per week, or non-stop until they burn out.
Different software development methodologies help to structure the work. For example, they assist the project managers in outlining which part of functionality will be done, in what time frame, and when to show results to owners.
Here are the top software development methods according to GoodFirms. They are the most frequently used by companies, so they’ll be represented to you along with some others.
Best software development process methodologies (Source: GoodFirms)
#1. Agile as a Prominent Software Development Methodology Example
Agile methodology SDLC is among today’s most popular software development approaches, accepted in all-size companies — from tech startups to Apple. Even government software is developed with Agile (acceptance rate) as one of the most applicable software engineering methods.
Instead of building the entire product in one Waterfall-like go, Agile splits development into a few iterations called sprints. Usually, one sprint lasts 1-4 weeks in this popular one of software methodologies. During that time, the development team designs, codes, and tests complete features that can be released as a working product.
The sprint's goal is to deliver a working product. For example, if the team dedicates a sprint to a single sign-on, this feature must be tested and work properly by the end of the sprint.
After the first release, the team collects feedback and plans the second sprint.
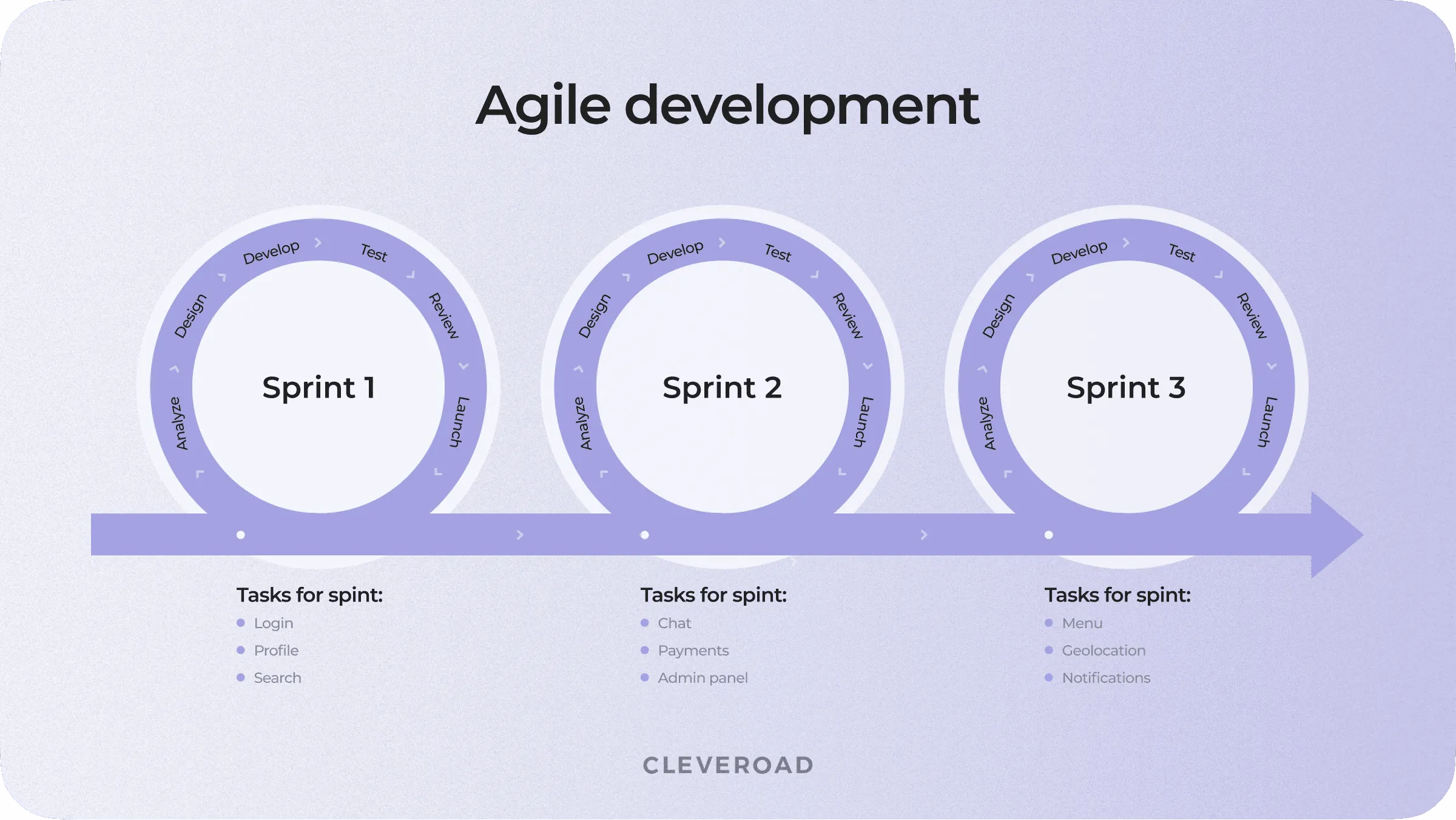
Agile development goes in short (1-4 weeks) sprints
Sprints work great on complex or lengthy projects (300+ hours) or when it's not clear what exact steps to take to get the result.
By splitting huge tasks into smaller sprints during this type of software delivery methodologies, the team can make releases more often, collect more requirements and feedback, and reduce the risks of not meeting users' expectations.
Agile benefits:
- Frequent releases (1-2 per month)
- Flexible, easy to make changes
- Each sprint of this type of software design methodologies ends with the release of a working product
- Client is more engaged in the development so there's a higher chance all their requirements will be met
- Team works closely and has a clear vision of their responsibilities
Drawbacks:
- Requires careful management
- No end-date for the development, no final price tag
- Requires experienced and responsible team members
Most software development companies that choose Agile from a bunch of software development frameworks and methodologies have Project Managers to watch over the team and reports the process to company's clients.
Use the Agile benefits for business
Apply to Cleveroad — we’ll give you an in-depth consultation on how to do it in the most proper way
Agile Framework #1 — Scrum
The difference between software development methodologies and frameworks is that the latter is a bit more formed approach with strict rules.
As with Agile, all the work in Scrum is split into sprints. Each sprint starts with planning and ends with the delivery of a stable, working product.
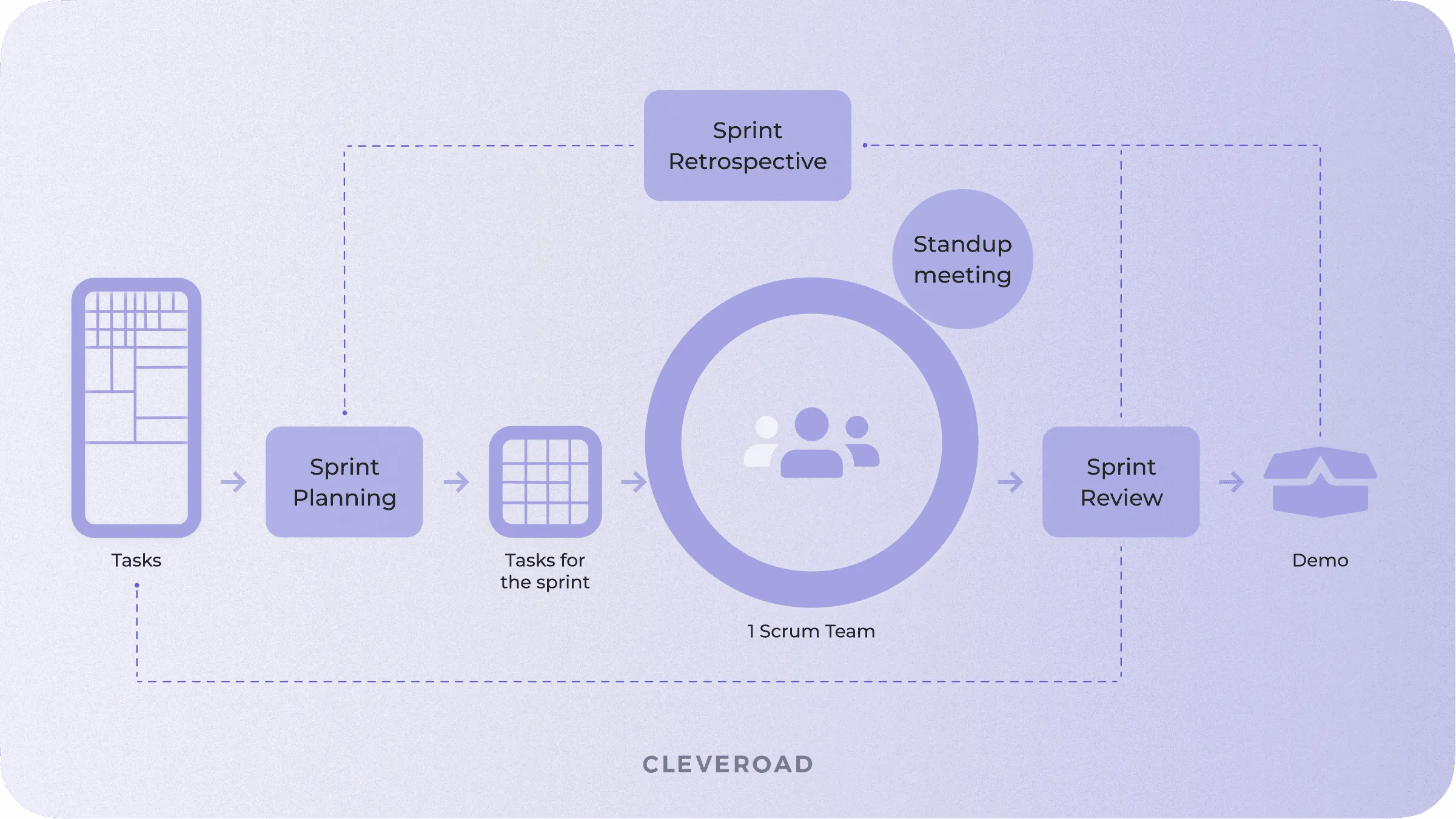
Scrum methodology for software development process
Essential Scrum elements that help the team remain flexible and quickly react to client's feedback:
- Sprint planning. Before the development starts, the team gathers for a meeting with clients to prioritize features and plan the next 2-4 weeks of development.
- Daily meetings/standups. Every morning, team members share their progress on tasks, plans for the current day, and possible blockers.
- Demo. Project Manager reports to the clients on the work done and gathers their feedback.
- Retrospectives. The team holds a meeting to discuss what's gone wrong during the sprint, what can be improved, and how.
All these meetings and discussions help to control the team, define blockers, and build better relationships with the client.
Scrum requires high involvement from the client's side and careful sprint planning. It's an excellent framework for quick MVP development and regular improvements.
What's an MVP and how to build it? Check our detailed guide on how to develop an MVP, including its benefits.
Scrum pros:
- Release a working product every 2-4 weeks
- Works with incomplete requirements
- Very flexible, easy to make changes
- Frequent meetings with the team
Cons:
- Doesn’t suit teams with insufficient self-discipline
- Requires high client involvement
- Needs contribution from every team member
Agile Framework #2 — Kanban
Kanban is even more flexible than Scrum as the team is only focused on the work which is currently in progress.
How Kanban works:
- The project is divided into stages and tasks.
- Tasks are marked with cards.
- The work process is divided into columns (at least three) — To do, In progress, Done.
- As developers work on tasks, they move cards between columns, from left to right.
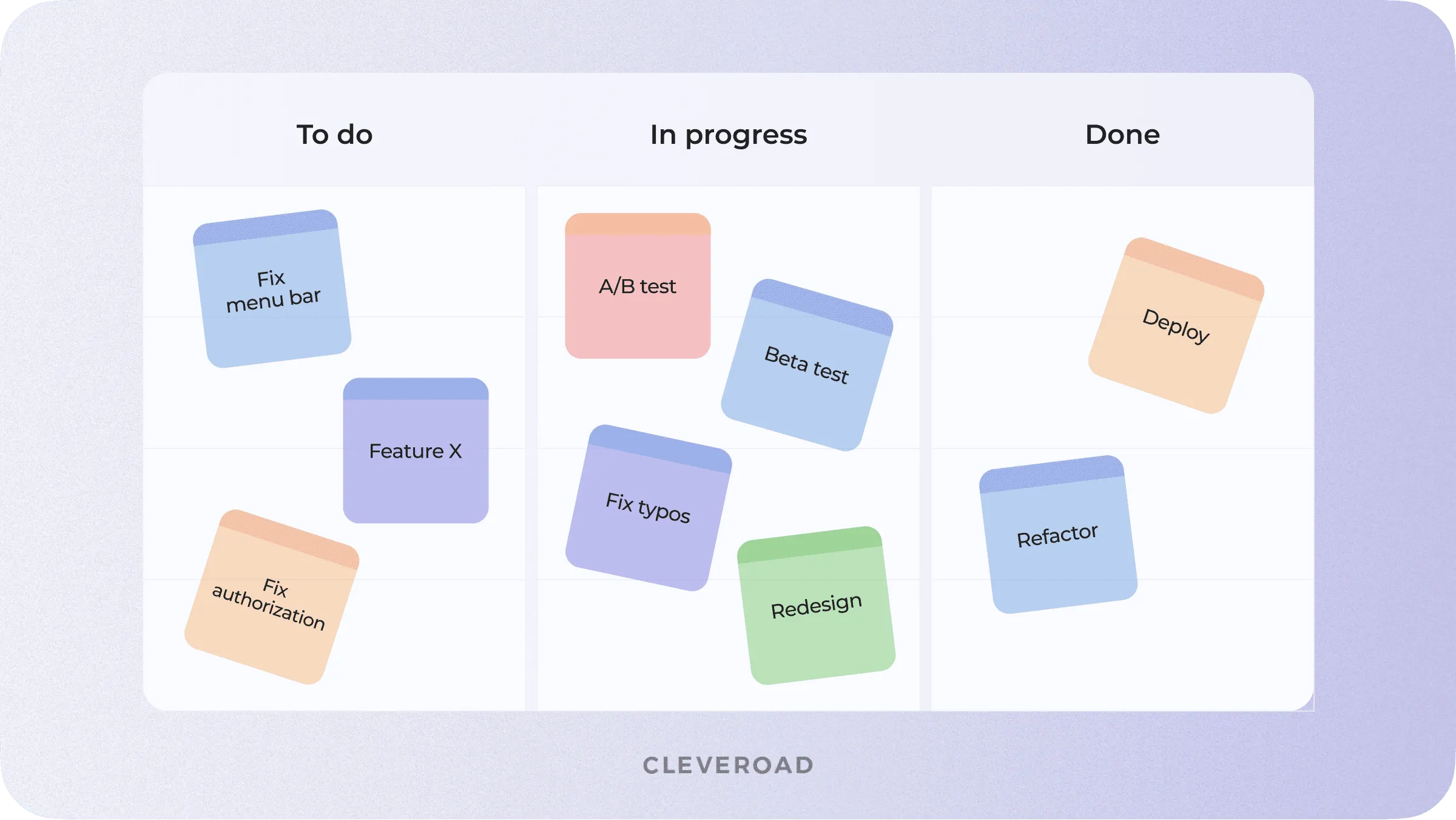
Kanban is one of the most flexible types of software development process
In most cases, a to-do list is organized as a Trello or Jira board. But in fact, you can even use a physical board with colorful stickers.
Kanban shares a few rituals with Scrum — daily standups, demos, retrospectives.
Still, unlike Scrum, Kanban doesn’t have any sprints or sprint planning meetings. As soon as the team completes a user story (part of functionality), the Project Manager creates a new task and places it on the board. This way, the team can make releases more often, up to 1-2 times per week.
Kanban pros:
- Simple task management
- Great flexibility, no sprints or sprint planning
- Good for projects under maintenance
- Doesn’t need re-planning when requirements change
Kanban cons:
- No sprints which can lower developer productivity
- Requires self-management skills from programmers
- Hard to control the scope of work
Agile Framework #3 — Extreme Programming
Extreme programming (XP) approach rather focuses on engineering practices than on project management.
XP is a set of best development practices, namely:
- Test-driven development. Programmers start with writing acceptance tests, not code.
- Code audit services. Fellow programmers check each other's code for mistakes.
- Refactoring. Restructuring existing computer code.
- Pair programming. Two developers work on the same functionality in turns.
- Continuous integration. New code pieces are constantly being built into existing ones.
- Unit testing. Automated testing that determines if the developed feature works properly.

Core practices of extreme programming framework
Only a small percentage of teams use the full range of XP practices on one project. Usually, they choose one or a couple of practices that’d work for their specific case.
Similar to Scrum, Extreme Programming starts with planning. The team analyzes requirements and prepare software development time estimation breaking down the whole project into set of tasks. Then, they agree on time frames with the client and get to work.
But instead of writing code first and testing it second, developers start with creating acceptance tests. These tests define exactly what the code must do according to the requirements.
After writing the acceptance test, two developers sit together to write a piece of code and run it through these tests. Developers work in turns. One programmer offers a solution, the other one comments on it and corrects errors. Then they change places and start all over again.
XP advantages:
- Clear code
- Fast to deliver an MVP
- Less documentation required
- Easy to adapt to ever-changing requirements
Disadvantages:
- High rate of client involvement
- Pair programming takes more time
- May not be enough documentation
You can learn more about our Agile-based software development process in our article
#2. Famous Software Design Methods: Waterfall
Waterfall used to be a 'classic' development approach for a long time: from 70x till 00x. This one of the methodologies (software development) is quite strict and linear, and every stage has its set deliverables. In Waterfall, the process goes only forward: a new stage starts only when the previous one is finished. For example, if you're at the coding phase, there's no way you can get back and change something in the product's design.
Waterfall-based development goes in six stages:
- Discovery. The team gathers a full list of requirements for the entire project.
- Design. Solution Architects define how to build the software and how it's going to work.
- Coding. Developers implement UI design according to client's requirements.
- Testing. QA engineers check the whole codebase for bugs or inconsistencies.
- Deployment. Developers integrate various pieces of the product and show its demo version to stakeholders.
- Maintenance. The team provides support and fixes bugs.

How Waterfall, popular software development method, works
Waterfall offers predictability, thus, more accurate budgeting and scheduling. It's perfect for fixed-price projects or enterprise-level software that requires very detailed planning and documentation.
Benefits:
- Simple, functional, gradual, and analytical methodology
- Great for fixed-price projects or the ones that require detailed documentation
- Requires less client involvement after the discovery stage
- Easier to estimate the final budget/schedule
Drawbacks:
- Needs exact requirements for the entire project
- Requires a lengthy discovery phase
- Not flexible, hard to make changes after the planning stage
- The final product may not meet the client expectations
With the lack of flexibility, Waterfall has almost been replaced by more responsive software engineering methodologies like Agile. There’s a good reason for that: Agile success rate is more than 1.5x higher than those of Waterfall projects (42% success rate of Agile vs. 26% Waterfall).
While the Agile failure rate is almost 3x lower compared to Waterfall. That explains why more and more companies switch to Agile and even consider it to be a standard.
#3. Lean Development Methodology
Lean is similar to Agile when it comes to flexibility, but still, these are two different software development methodologies. Let’s research them in comparison and see why Lean and Agile are various.
Here’s the difference according to Mary and Tom Poppendieck, creators of 'lean' software development methodology definition:
| Aspect | Lean | Agile |
Client | Create value for the customer; focus only on value-adding activities | Have a working product that fulfills customer's needs |
Development speed | Rapid value creation, short cycle times | Continuous delivery of a working product |
Lean methodology software approach is often referred to as the MVP strategy. Under Lean, a team releases a bare-minimum version of the product, learns from user feedback, then makes improvements or changes based on this feedback.
There are seven Lean practices focused on software teams and users:
- Eliminate Waste. In software development, wasteful activities may refer to extra features, partially done work, delays, defects, and so on.
- Deliver Fast. Build an MVP product in the minimum time possible, finding the things that slow down the team and eliminating them.
- Delay Critical Decisions. Don't make a vital decision until you have all the information in hand.
- Amplify Learning. Gather feedback to adjust the software to users' needs.
- Build Quality In. Work on software quality at the coding level.
- Optimize the Whole. Focus on improving the entire workflow, instead of just one part of it.
- Respect People. Encourage healthy and productive discussions among team members.
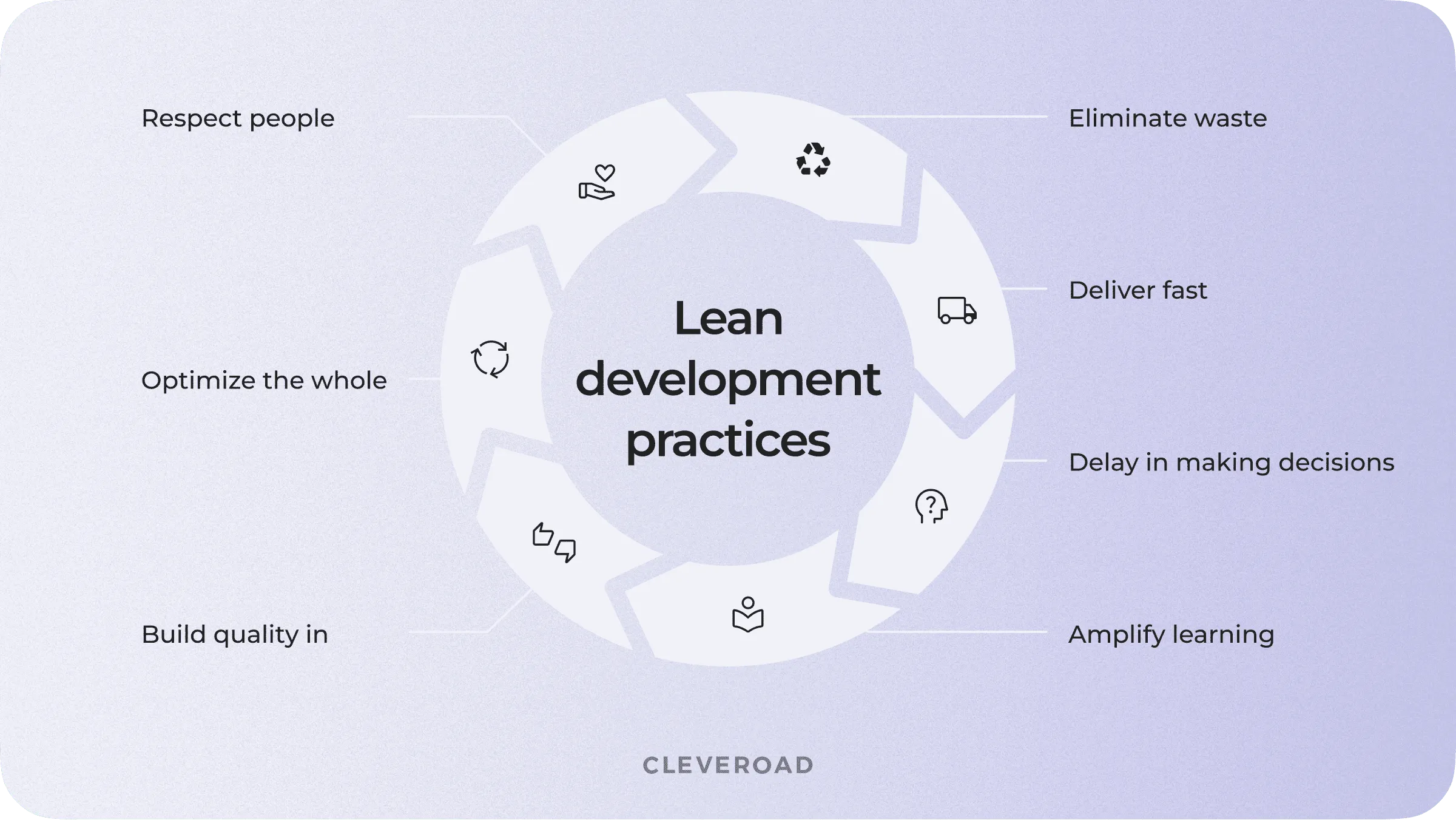
Lean is one of the best software development methodology for startups
Lean as one of the methods of software development is trendy among startups that haven't yet come up with a finished product. By launching with MVP features only, they have a chance to learn more from real market metrics. They find out what works for users and what doesn't and then roll out new updates to fix or improve the software.
Lean pros:
- Works for early-stage startups
- Focuses on rapid development and improved efficiency
- Shortest time-to-market
Lean cons:
- The client needs to trust the team’s decisions
- Need detailed documentation
- Business Analyst must be involved to document requirements
Explore the Advantages and Disadvantages of Lean Startup to decide whether this concept suits your project
#4. Types of Methodologies in Software Development: Feature-Driven Development
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) is a combination of several development approaches and techniques into one to organize software development around its features and to produce workable products as soon as possible. Such software development methodology is typically used by large teams working on project- or object-oriented technologies and businesses switching from stage-based to iterative methods.
It contains five necessary steps to perform: model creation, functionality list development, planning, design, feature encoding.
FDD methodology in software development benefits:
- Built on established software development standards
- Employing industry-recognized best practises
- Assists in advancing significant projects which are successfully ongoing
FDD drawbacks:
- Complex to realize and inappropriate for smaller projects and teams
- Needs to be tracked over at every stage
#5. Rapid Application Development as One of The Modern Software Development Methodologies
Rapid Application Development (RAD) helps the developers produce qualitative software quickly prioritizing user feedback above planning. This type of methodology concentrates on quick prototype releases and iterations with the aid of other development methodologies.
Acting upon this software development methodology, the team passes the following stages of product creation: analysis, interface creation, cycles of prototypes, testing services, software launch and integration.
Advantages:
- Transparency of client-developer communication and frequent feedback
- Solution creation is sped up due to less documentation and preparation process
- Decreasing the likelihood of poor performance thanks to ongoing client input and early bugs finding
Disadvantages:
- Relatively new software methodology, and risky, as a consequence
- Not appropriate for projects with minimal budgets due to modelling and automated code production expenses
#6. DevOps Software Methodology
Some of the researchers call DevOps software dev methodology; however, it's more correct to call it a set of activities designed to complement an organization's culture. Such a set makes possible an organizational transformation that enhances communication across the different project lifecycle divisions, including development, quality assurance, and operations.
What is software development methodologies (like DevOps) pros:
- Time to market acceleration
- Failure rate of new releases is lowered
- Increasing reliability of the development flow
DevOps cons:
- The delivery pipeline is slowed down by the need for human contacts to achieve particular quality features.
- Problems may also arise if different departments use different environments.
Software Development Processes and Methodologies: Full Comparison
What is the best software development methodology or framework to follow? It depends on your project. There’s no universal strategy applicable to just any situation.
If you're working on a startup, it may be better to go with Agile or Lean methodologies in software engineering because of their flexibility—you can change the work scope at any time. In case you're improving an enterprise-level desktop app where managers demand strict and detailed documentation, you may choose Waterfall. It’ll seem the best methodology for software development in this case.
For you to simplify your choice of the best software management method, we’ve made a methodology comparison table.
| Name | When to apply | Client involvement |
Agile | For any-sized projects | Client provides requirements & feedback |
Scrum | Long-term, complex projects | Client places the leading role is defining the requirements, providing feedback |
Kanban | For fixing bugs, small releases and adapting to changing priorities | Owner sets tasks & provides feedback |
Extreme programming | Write code within strict timeframes | Client takes part in defining the requirements, estimation and prioritization |
Waterfall | For fixed-size projects; enterprise software with clear requirements | High during the discovery stage; lower in the next phases |
Lean development | For MVP startups | Client provides input on sample screens and initial user stories |
Feature-Driven Development | For large teams conducting complex projects | During reporting, the client is a participant in the development flow. |
Rapid Application Development | Provide something that functions under pressure or in case of a strict deadline to meet | Clients collaborate with the developers to guarantee that their needs are addressed at every stage of the creation process. |
DevOps | Reduce the time required to deploy software and automate deployment and testing | Companies communicate with their consumers using software offered as online applications or services and on a variety of devices. |
This table includes only the most popular methodologies for software development chosen by different IT companies. If you want to know more, you can contact our experts for a profound consultation as to such an essential choice.
How to Choose Software Dev Methodology For Your Project: Hints to Consider
We’ve told you about the most widespread methodologies for software creation, but there are dozens of them used by various IT companies. Here the question arises: how to choose the methodology in software engineering that will best fit your project?
We’ve conducted our research and defined what points you should be aware of before choosing the appropriate software development methodology.
Think out how flexible your project requirements are. The flexibility of your software project requirements should be taken into account when choosing a certain software design methodology. For example, if you plan to start web or mobile product creation requiring modifications during the development process, you should better choose Agile. If your software development process is more stable and predictable, you can apply to Waterfall.
Evaluate the future size of your project while making software development methodology comparison. Each of the methodologies calls for a specific number of developers on the team. This factor, in its turn, depends on the project size. So, for example, large projects require more software dev team members and more complex methodologies to manage the workflows.
Define the end users for your digital product to understand what software development methodology is right for your particular project. Is your product intended for a specific user base with a definite set of needs? Waterfall methodology will be helpful for you. Your audience is wide, and your app will need more features after its launch. In this case, Agile will be the most advantageous choice allowing you to step back and make necessary changes.
Orient the length of your software development flow. Iterative-based types of software development methodology like Agile, are appropriate for releasing product's functionality fully or partially regarding fast-approaching deadlines. The Waterfall technique is the greatest option if the time period for software development is long-term without impending deadlines.
You can also facilitate your task as to the selection of the project methodology, and apply to a skilled software development vendor working upon already chosen methodology and capable to help you with your own project development. They’ll eagerly tell you what software methodology is appropriate for your particular project and why, as well as help you with the successful product development.
Why to choose Agile software development methodology if you develop a mobile app? Read more in our guide!
Your reliable software development vendor
These days’ software development practice has proved that Agile methodology is the best way to quickly and effectively build digital products. Cleveroad totally agrees with this.
Cleveroad is an experienced software development provider located in the CEE region and helps startups, small and midsize businesses (SMBs), as well as large enterprises gain a competitive edge and boost their performance through qualitative software delivery breathing life into bold concepts.
Working with us, you will get the following benefits as:
- Profound consultations with one of our specialists (Project Manager, Business Analyst or Solution Architect) as to the choice of appropriate software development method of your company requires
- Flexible models of cooperation to meet your requirements
- Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) signing per your wish
- Fast development process based on the best software methods without any bureaucracy or hidden costs
- Innovative technology stack combined with cutting-edge development methods
- Proven comprehensive experience in numerous business industries (e.g., logistics, healthcare, fintech, entertainment, education, etc.)
- Software development teams consisting of skilled individuals capable to quickly adapt to project changes
- Quality assurance and control on every step of the product development
- After-development maintenance, support, and promotion services, and other on-demand services
At Cleveroad, we follow Agile and apply the Scrum framework to our everyday processes. As we often deal with tech startups, Scrum helps our clients remain flexible and easily apply changes to their projects.
That’s how we’ve helped to launch different projects for our clients—and keep helping to improve them. The latest of them built according to Agile are the following:
Quality Management System (QMS) — a B2B SaaS platform for manufacturers of medical devices. It assists them in automating paperwork, as well as streamlining workflows connected to ISO and FDA certification essential to produce medical gadgets.
We also work on a web-based marketplace for the US and European B2C clients, which will help unite both merchants and their customers in one digital environment.
One of our projects is a clinic management platform ordered by a rehab services provider in order to offer remote care and services for their patients. The system also offers an opportunity to create and schedule appointments, manage customers and workflows in frames of one software solution.
You can get acquainted with more of our finished projects in our portfolio. We can also conduct a software development process for you making it effective and quick thanks to Agile methodology used during our digital products’ creation flow, and deliver a cutting-edge and profitable product matching your business needs.
Skilled vendor is eager to help you
Our team will help you create your solution considering the best development practices
In short, a development methodology is a process of how to build your software. For example, you can go from planning to release step by step (Waterfall methodology). Or release a small part of functionality every few weeks (Agile).
Development companies apply different software development methodologies and frameworks. They help to standardize the process, making it clear what’s going on with the product for both clients and internal teams.
There's no universal methodology. To choose the right approach, you should clearly define the goal of your project. When you have strict requirements for your project it'll be easier to figure out what is methodology in software engineering that will be the most appropriate for your business needs.
There are a lot of software development methodologies used by different programmers. Even you can create your own methodology that will boost your software development process.
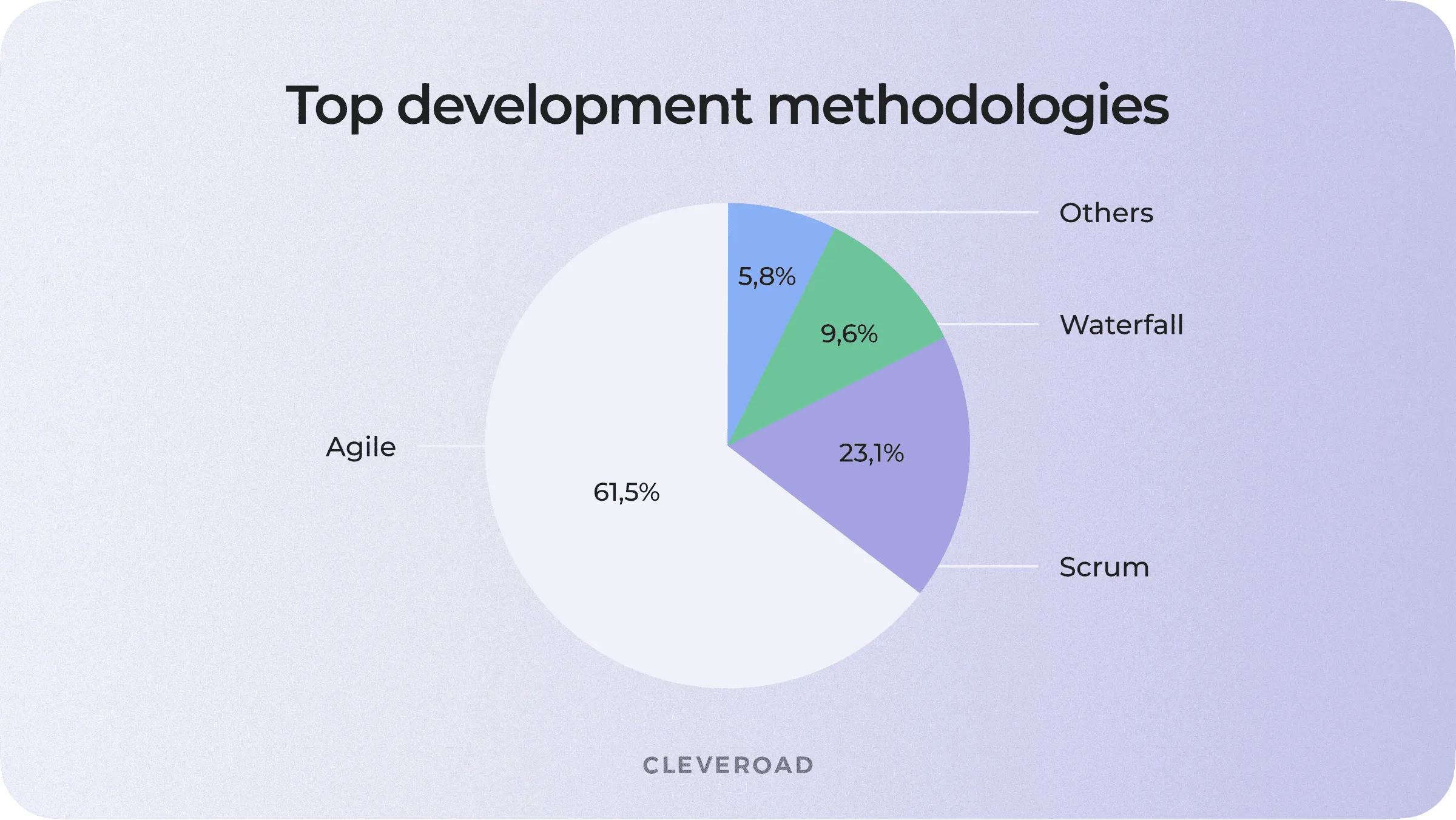
However, if we're talking about what is the best software development methodology, here are the numbers:
- Agile — 61.5%
- Scrum — 23.1%
- Waterfall — 9.6%
- Others — 5.8%
Two most common software development methodologies are Waterfall and Agile.
Yes, and it still covers lots of projects. For today, Waterfall is the second-popular methodology after the Agile and Scrum framework.
What are the software development methodologies most popular according to GoodFirms:
- Agile — 61.5%
- Scrum — 23.1%
- Waterfall — 9.6%

Evgeniy Altynpara is a CTO and member of the Forbes Councils’ community of tech professionals. He is an expert in software development and technological entrepreneurship and has 10+years of experience in digital transformation consulting in Healthcare, FinTech, Supply Chain and Logistics
Give us your impressions about this article
Give us your impressions about this article
Comments
4 commentswow, Amazing! really very helpful article for increase our knowledge
liked your guide very nice
liked your blog very informative. A very great post. Many thanks for sharing this pieces. 2021 is really going to be a Digital Transformation year so thanks for informing
thank you for sharing the article, it really helped me a lot. I used to think that lean is just another agile framework not a methodology itself, thanks for spelling this out.