The Ultimate Guide to ERP Software Development for 2026: Stages, Benefits, and Estimated Price
Updated 23 Dec 2025
18 Min
3930 Views
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software helps organizations centralize operations and maintain control as complexity increases. It replaces scattered tools with a scalable system and relies on solid domain expertise. As operations expand, spreadsheets and disconnected systems create data silos and increase errors. At this point, adding more people no longer fixes the problem. ERP software development becomes a strategic step that automates core operations and standardizes workflows across departments.
At Cleveroad, we’ve been delivering ERP system development projects across various industries and business sizes for over 15 years. We design ERP solutions that reflect real operational workflows, with a strong focus on process analysis and modular architecture, so systems remain flexible and scalable as businesses evolve.
Based on our experience, we've prepared an in-depth guide on ERP development. In this guide, you’ll learn how to successfully complete the key steps of building enterprise resource planning software:
- Define clear business requirements and project scope
- Map processes and structure ERP modules correctly
- Design a scalable system architecture and tech stack
- Build and integrate ERP modules into a unified system
- Migrate data, test the system, and deploy it safely
- Train users, launch the ERP, and scale it over time
To recognize these steps in detail, read our article.
What Is ERP Software and How Does It Work?
ERP software is a centralized system that manages core business processes in real time, including finance, supply chain, HR, inventory, and operations. Companies use this software to collect and manage business data in one place, instead of relying on separate tools for each department. Such an approach ensures that all teams work with consistent, up-to-date information.
ERP works through a modular structure connected to a shared database. Each module supports a specific function and gives teams access only to the data they need, while managers and executives see the full operational picture. When data changes in one module, it updates automatically across the system, improving accuracy, speeding workflows, and enabling better decision-making.
What makes ERP different from CRM or BPM
ERP, CRM, and BPM systems address different business problems, even though they often integrate with one another. They differ in such ways:
- ERP software manages and synchronises core internal operations across the entire company;
- CRM systems concentrate on customer-facing processes such as sales, marketing, and support;
- BPM tools help model and automate individual business processes without acting as a system of record for enterprise data.
From a software development perspective, ERP system development creates the operational backbone of a company, CRM enhances customer interactions, and BPM improves how specific processes run across systems.
Let’s look at the compassion table that shows the main differences between ERP, CRM, and BPM:
| Software specification | ERP software | CRM software | BPM software |
Main focus | Core operations | Customer relationships | Business workflows |
Data | Centralized | Customer-centric | Process-level |
Scope | Company-wide | Sales and support | Individual processes |
Best for | Full operational control | Revenue and retention | Process optimization |
What Business Problems Does ERP Solve?
ERP systems address operational problems that emerge when growing businesses rely on disconnected tools and manual coordination. These issues slow decision-making, increase costs, and limit visibility across departments.
Let’s review how ERP software addresses common business challenges.
Removing data silos across departments
When departments rely on separate systems, data duplication and communication delays become unavoidable. Teams work with inconsistent data, repeat the same tasks, and make decisions without a full operational picture.
Integrating ERP software centralizes business data and enables cross-departmental access through a shared database, significantly improving information flow and collaboration. Research by JCIS shows that ERP integration reduced data redundancy by 60% and improved information sharing efficiency by 45% in small manufacturing firms.
Improving financial control and reporting
Disconnected accounting tools and manual reconciliation make it difficult to maintain accurate financial oversight as companies grow. Finance teams struggle with delayed close cycles and limited visibility into real-time financial performance.
ERP system development allows for standardizing financial workflows and automating reports across business units, which improves accuracy and control. A BPM study found that ERPs raised financial efficiency scores by 28% across firms in Portugal, Spain, and Finland.
Preventing inventory losses
Poor inventory visibility leads to stockouts, excess inventory, and higher carrying costs. As a result, companies either lose sales due to unavailable products or tie up capital in slow-moving stock.
Development of ERP systems allows for the integration of demand planning and procurement to provide real-time inventory control. Researches confirms that ERP-enabled firms reduced inventory holding costs by 20–25% while improving turnover ratios by 15% (Source: JOM).
Reducing manual work and errors
Manual data entry across multiple systems increases labor costs and operational risk. It also leads to frequent data inconsistencies, human errors, and time lost on corrections and reconciliations.
Development of ERP system automates data flows between departments and eliminates repetitive tasks. Bradford and Florin report that ERP application adoption reduced manual work by 50% and accelerated reporting cycles by 37% across departments (Source: Bradford & Florin).
Supporting scaling and fast growth
As companies scale, fragmented systems struggle to support higher transaction volumes and organizational complexity. This often forces teams to rely on temporary manual workarounds that slow operations and increase the risk of errors.
ERP development provides a standardized operational backbone that supports growth without increasing operational overhead. Studies found that ERP-enabled firms scaled operations 27% faster and expanded 40% more effectively than non-ERP peers (Source: Bradford & Seong).
Enhance your company’s performance with our ERP development services. Benefit from seamless cross-departmental collaboration with real-time data and reduce costs
Should You Build a Custom ERP or Use an Off-the-Shelf Solution?
When turning to ERP system development, entrepreneurs have two different options. The first one is to use third-party software distributed via different subscription plans. The second one is to create a custom solution for the company. Both approaches have some flaws and advantages, so now, we review each ERP development option:
Off-the-shelf solution
Software as a service providers offer a number of ERP solutions that can be deployed right after the initial payment. Turn-key solutions like Acumatica, Sage Intacct, and SAP Business One are a good fit for small and medium-sized businesses. At the same time, extensive systems like Oracle NetSuite, SAP S/4 HANA, and Microsoft Dynamics are designed for large businesses and enterprises.
Even though some of these systems, like SAP S/4 HANA, let users create custom add-ons to the core software, they still lack flexibility. Additionally, manipulations with source code and API integrations mean that you should have developers at your side.
Among all the pitfalls, training difficulty is the one that hurts the most. If you’re an owner of a small company, most likely, you can figure out the software peculiarities on your own. However, if you’re managing a large company, the process of integration may take months or even years. So, if you’re aiming at third-party software just because of the integration speed, think twice before paying.
Custom ERP solution
If third-party solutions are limited to what was intended by their developers, custom-made software solutions are limited only to your imagination. Consider it a clean piece of paper where you can draw anything you want. Customized ERP features for accounting entries, supply chain management software features, or precise lead analysis for the sales department. Custom solutions let you create a symbiosis between your departments.
Moreover, it may appear that third-party solutions contain useless features for your businesses and don’t have the ones you need. Custom ERP software development guarantees that you’ll get what you need (if you’ve drawn up the feature list correctly).
Detailed documentation created by engineers during development will help responsible employees to fix unexpected issues without contacting third-party vendors. Besides, you can hire a technical writer who’ll cooperate with developers and write a comprehensive manual for the whole system. It’ll speed up the training process and help new employees understand the workflow.
Below you can find a table that summarizes all of the differences between an off-the-shelf solution and custom ERP development:
| Criteria | Off-the-shelf ERP solution | Custom ERP solution |
Deployment speed | Faster initial setup | Longer initial development |
Flexibility | Limited to vendor features | Fully tailored to business workflows |
Customization | Add-ons and APIs only | Any logic, module, or flow |
Feature relevance | Includes unused features | Only needed functionality |
Integration | Often complex and restricted | Built for existing systems |
Scalability | Depends on vendor limits | Scales with business growth |
Training effort | High for large teams | Simplified with tailored UX |
Ownership | Vendor-controlled | Fully owned by the business |
Maintenance | Vendor updates and policies | Internal or partner-managed |
Best for | Standard SMB operations | Complex or growing businesses |
Core Modules You Need in Your ERP Software
ERP systems deliver value when core business functions work within a single, connected platform. Each module handles a specific operational task and shares data with other modules through a unified architecture. This approach eliminates fragmentation and ensures consistency across the organization.
Below are the essential ERP modules most businesses need, along with what each covers.
Finance and accounting
The finance and accounting module manages the general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting. It gives finance teams real-time visibility into cash flow, costs, and profitability across departments.
By connecting financial data with sales and procurement, this module reduces manual reconciliation. It also supports compliance, audits, and faster financial close cycles as the business scales.
Procurement and purchasing
The procurement and purchasing module controls supplier data, purchase requests, approval workflows, and purchase orders. It enforces standardized purchasing processes and ensures compliance with internal policies.
Integration with inventory and finance allows companies to track spending in real time. This visibility helps optimize supplier selection, negotiate better contracts, and avoid uncontrolled purchases.
Sales and order management
Sales and order management handles quotations, pricing rules, sales orders, and fulfillment tracking. It ensures that customer orders move seamlessly from sales to inventory, warehouse, and finance teams.
By automating order workflows, the module improves order accuracy and processing speed. It supports complex pricing, discounts, and multi-currency transactions. Sales teams gain visibility into order status and availability. Customers benefit from faster and more reliable fulfillment.
Inventory management
ERP inventory management tracks stock levels, movements, and valuation across locations and warehouses. It maintains accurate, real-time records of raw materials and in-transit inventory.
When connected to sales and production modules, inventory management aligns supply with demand. This reduces stockouts and prevents excess inventory, especially for businesses with the complex supply chains.
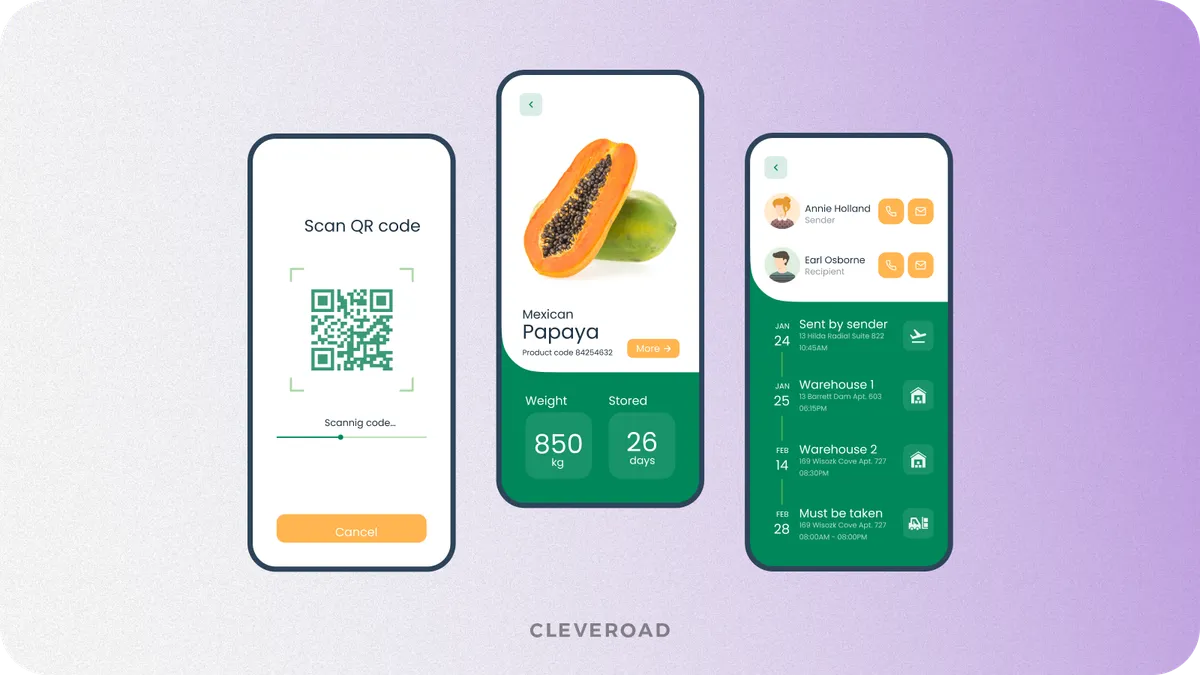
Inventory management module for mobile version developed by the Cleveroad team (Source: Dribble)
Human resources management
The human resources module manages employee records, payroll, time tracking, and benefits administration. It centralizes workforce data and standardizes HR processes, reducing manual paperwork and administrative overhead.
Integration with finance and operations links labor data to costs and productivity. Companies gain better insight into staffing needs and workforce expenses. The module supports compliance with labor regulations and internal policies.
Customer data management
Customer management stores customer profiles, contracts, communication history, and billing information. It ensures that all teams work with consistent customer data. Sales, support, and finance share the same customer view.
When integrated with sales and accounting, customer management reduces billing errors and disputes. Teams respond faster to customer inquiries with full context. The customer management module supports long-term relationship management and retention strategies.
Warehouse management
Warehouse management oversees picking, packing, shipping, and internal stock movement. It tracks inventory at a detailed level, such as bins, pallets, or zones. This precision improves control over warehouse operations.
When connected with inventory and sales modules, the warehouse management system module speeds up fulfillment. Module picks and ships orders based on real-time data. It improves accuracy and reduces delivery delays.

Warehouse management module developed by the Cleveroad team (Source: Dribble)
Production and manufacturing
ERP systems include a production and manufacturing module that supports production planning, bills of materials, routing, and shop floor control. It connects manufacturing operations with inventory and procurement data.
Manufacturers get visibility into production schedules and capacity utilization. The production and manufacturing module allows the manufacturer to align demand with available resources. It also improves traceability and quality control across production stages.
Reporting and analytics
Reporting and analytics aggregate data from all ERP modules into dashboards and reports. They provide real-time visibility into financial and performance metrics. Decision-makers no longer rely on delayed or manual reports.
This module supports KPI tracking and forecasting. Executives obtain a holistic view of business performance across departments. Potential risks and inefficiencies become visible early. This enables faster, data-driven decisions and continuous improvement.
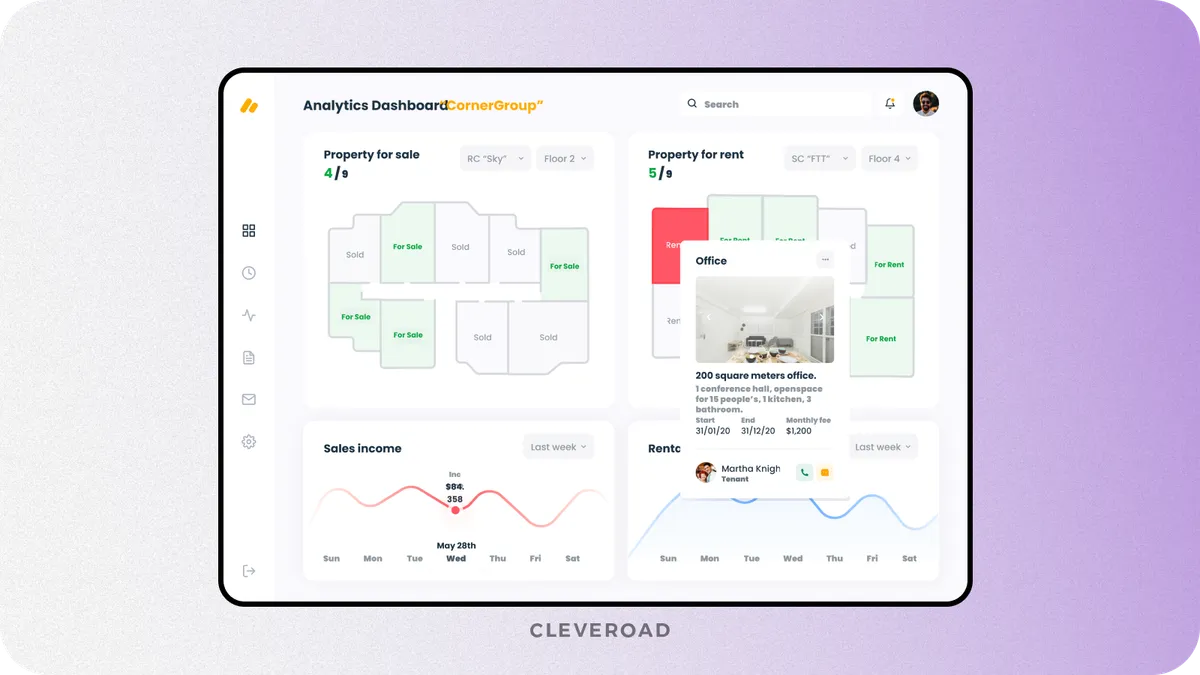
Reporting and analytics module developed by the Cleveroad team (Source: Dribble)
ERP System Development Process: From Idea to Implementation
Enterprise resource planning software development follows a structured sequence of steps that align technology with real business operations. Each phase minimizes the risk of failure by applying best practices and facilitates sustainable growth through proactive planning.
Below is a detailed breakdown of each ERP system development step and the best practices Cleveroad uses to complete them successfully.
Step 1. Requirements discovery and business analysis
The first stage of the ERP system development focuses on understanding business goals and operational pain points. Teams conduct stakeholder interviews to gather functional and non-functional requirements. Experts review current workflows to see how processes run at the current moment. This prevents assumptions that later cause rework.
At Cleveroad, we start ERP projects with a deep solution design workshop. Our analysts map operational flows and identify gaps between current tools and business needs. Such an approach allows us to define realistic priorities and build an enterprise resource planning system aligned with your actual workflows.
By the way, our solution design workshop is free. Book a call with our experts now to discuss your business challenges and ways to solve them with ERP software.
Step 2. Process mapping and scope definition
Process mapping visualizes how data and tasks move across departments. At this stage, specialists define user roles and interaction scenarios in detail. Specialists clarify relationships between ERP modules early. This prevents conflicts between departments later.
Cleveroad documents process maps and module dependencies in a structured way. We define scope boundaries based on business impact and technical dependencies. This approach protects projects from scope creep and budget overruns. Clients clearly understand what will be delivered and when.
Step 3. System architecture and tech stack design
This step outlines how the ERP system will work technically. Architects select appropriate system architecture based on scalability and performance needs. Experts choose module structure, APIs, integration logic, and more.
Cleveroad designs ERP architectures with modular growth in mind. We select tech stacks based on workload and long-term support needs. Our teams responsible for APIs and security work together from the beginning to create a stable scaling environment.
We’ve explained how to build an ERP system from scratch and how much it costs in our step-by-step guide
Step 4. UI and UX design for all user roles
Design teams create interfaces tailored to different user roles. Wireframes and prototypes show navigation, screen logic, workflows, and more. Stakeholders validate designs before development starts. Such an approach avoids usability issues after launch.
At Cleveroad, our UI and UX designers work closely with analysts and engineers. We design ERP interfaces for clarity and speed under real working conditions. Our focus stays on reducing clicks and errors, which will improve adoption and daily productivity.
Step 5. Module development and internal integrations
ERP development involves building the most critical modules first and expanding the system in a multi-module structure. Teams create features in iterations with defined logic and validations, and each module adheres to shared architectural standards. This modular approach enables independent development and testing while ensuring all modules operate as an unified system.
Cleveroad has extensive experience in building complex multi-module systems, including large-scale platforms with sophisticated business logic and role hierarchies. For our client Prime Path Medtech, we designed and developed a web-based Quality Management System from scratch.
QMS has multiple interconnected modules, including document management, actions, training records, and HR, unified through a shared API layer and role-based access control. Modular architecture developed by our engineers enabled seamless internal integrations, consistent data flow, and automated certification workflows across organizations.
As a result, our client received a fully automated, scalable QMS that reduced operational overhead and improved transparency in the certification process.
Here is what Breanne Butler, Client Liaison Officer at Prime Path Medtec, says about collaboration with Cleveroad:
Breanne Butler, Client Liaison Officer at Prime Path Medtech™
Step 6. External system integrations
To operate effectively, the ERP system must be integrated with all your business systems. These may include CRM, accounting, warehouse, or e-commerce platforms. Developers implement secure API connections and synchronization rules to automate and ensure the reliability of data exchange.
Cleveroad has in-depth experience integrating ERP systems with internal and third-party software. We help businesses extend ERP functionality without overbuilding modules, while ensuring stable data exchange and error handling in production.
ERP integrations we work with include:
- ERP platforms: SAP, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Oracle ERP Cloud, Odoo, NetSuite
- eCommerce & marketplaces: Shopify, WooCommerce, Adobe Commerce, BigCommerce
- Finance & accounting: QuickBooks, Xero, MYOB
- CRM systems: Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM
- Supply chain & inventory: Oracle WMS, Zoho Inventory, SkuVault
- Logistics & shipping: Shippo, Shipify, LogistaaS
- Payments: Stripe, PayPal, Adyen, Braintree
- Asset & maintenance management: UpKeep, MaintainX, Asset Panda
Step 7. QA testing and security validation
Quality Assurance (QA) ensures that the ERP system works as expected. It includes functional testing of business logic, integration testing across modules, and performance testing to verify system stability. QA also identifies defects and inconsistencies before they affect daily business processes.
Cleveroad provides dedicated QA services for ERP projects. Our QA engineers validate business logic, integrations, and system behavior as a whole. This includes functional testing, integration testing, regression testing, load and stress testing, as well as security validation performed in parallel.
Such comprehensive testing ensures system stability, data integrity, performance under real workloads, and reliable operation of critical business processes after launch.
Step 8. Data migration and environment preparation
This step focuses on safely transferring data from legacy systems into the new ERP environment. Legacy data is reviewed for accuracy and relevance, then cleaned, standardized, and transformed to match the new system structure.
At Cleveroad, we start with a data audit before migration begins and plan the migration strategy alongside system deployment. Our team prepares server or cloud-based ERP environments in parallel, configuring security and performance settings in advance. We also test backup and recovery scenarios before going live. This approach ensures a stable and reliable production setup from day one.
Step 9. Deployment to production
Deployment moves the ERP system from the testing environment to production. Experts release modules in a controlled sequence to avoid conflicts. They also synchronize and verify integrations with external systems. Final readiness checks confirm system stability and performance.
Cleveroad plans deployments with rollback and monitoring strategies. Our teams closely monitor system behavior after launch and resolve issues immediately to avoid disruption. This approach minimizes downtime.
Step 10. User training and ERP onboarding
After ERP development, users receive role-based training tailored to their daily responsibilities. Teams learn how tasks and data flow through the ERP system. Practical sessions help employees work confidently in the new environment. This support remains available during the transition period.
Cleveroad provides structured onboarding assistance focused on system usage and workflows. We supply training materials and guidance to help teams get comfortable with the ERP. This reduces friction during rollout and supports smoother adoption across departments.
Step 11. Ongoing support and system scaling
Since launch, the ERP system requires continuous support and monitoring. Teams manage updates, bug fixes, and performance tuning. Security and system health checks run on a regular basis. Stability becomes the main operational focus.
Cleveroad provides long-term ERP support and scaling services. We add new modules and optimize performance as needs grow. Architecture supports expansion without disruption. This ensures sustained return on investment.
What Are the Main Risks of ERP Development and How to Avoid Them?
ERP projects often fail due to planning and change management gaps. Below are the most common ERP development risks and how the Cleveroad team mitigates them with the right approach.
Unclear scope and poor requirements
ERP projects fail early if business goals and requirements remain incomplete. Teams move forward with assumptions instead of validated needs. So, this leads to scope creep and budget overruns.
Cleveroad mitigates this risk through a structured Discovery phase that turns your ideas into a clear plan. Our team of experts analyzes business processes, refines requirements, and documents system logic, user roles, integrations, and non-functional needs. We validate features and UX before development starts and prepare a detailed cost estimate and timeline.
One of our clients, Betabox, highlights the Discovery Phase as a key reason for selecting Cleveroad as their technology partner, noting the depth of analysis and structured approach from the beginning:
Sean Newman Maroni, CEO at Betabox: Feedback on Cleveroad's EdTech Development Services
Weak integration and siloed modules
ERP systems lose value when modules function as isolated components. Poor integration causes data inconsistencies and manual workarounds. Departments continue operating in silos despite having an ERP. This undermines the purpose of the system.
Cleveroad designs ERP software solutions around unified data models and internal APIs. We plan integrations at the architecture stage, not after development. Modules exchange data through controlled interfaces. This ensures consistent data flow and end-to-end process automation.
Problems with data migration
Data migration often exposes hidden issues in legacy systems. Incomplete, outdated, or inconsistent data causes errors after launch. Poor migration planning can disrupt operations and delay adoption. Fixing data issues post-launch becomes costly.
Cleveroad runs data audits before migration begins. We clean, normalize, and test data through multiple migration cycles. Test environments validate accuracy before production launch. Such an approach minimizes risk and ensures data integrity.
Low user adoption after launch
Even well-built ERP systems can fail if users resist them. Complex interfaces and unclear workflows will slow daily work, and employees will revert to spreadsheets or legacy tools. This reduces ROI and creates shadow processes.
Cleveroad’s ERP system development process focuses on usability and change management. We validate workflows with real users, explaining how to use the system and why processes change. This increases adoption and long-term usage.
Over-customizing the system without a plan
ERP projects run into trouble when teams add custom logic without a long-term vision. Short-term fixes turn into permanent dependencies. Updates become risky and slow. Over time, the system loses flexibility and becomes costly to maintain.
Cleveroad prevents this by designing ERP systems around modular architecture and controlled extension points. We separate core logic from configurable components. Custom features align with business differentiation, not convenience. This allows the ERP system to evolve without costly rewrites.
Cleveroad as Your ERP Software Development Partner
Cleveroad is a skilled ERP software development company with more than 15 years of experience in the IT market. We help companies replace fragmented tools with scalable ERP solutions that reflect real operational workflows and support long-term growth. Cleveroad provides a range of software services, including custom ERP development, legacy system modernization, IT consulting, AI development, and integration.
When partnering with Cleveroad for ERP software development, you get:
- Proven ERP and business digitalization expertise across Healthcare, FinTech, Logistics, Retail, and other industries
- A team of 200+ engineers and consultants experienced in backend, frontend, mobile, cloud, and DevOps technologies
- We have experience integrating ERP systems with Oracle ERP Cloud, NetSuite, Odoo, Zoho, SAP, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, and more
- A cooperation with an IT partner with ISO/IEC 27001:2013 (security management) and ISO 9001:2015 (quality management) certifications
- Flexible cooperation models: Dedicated team, Staff augmentation, Project-based
- Signing a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) per your request
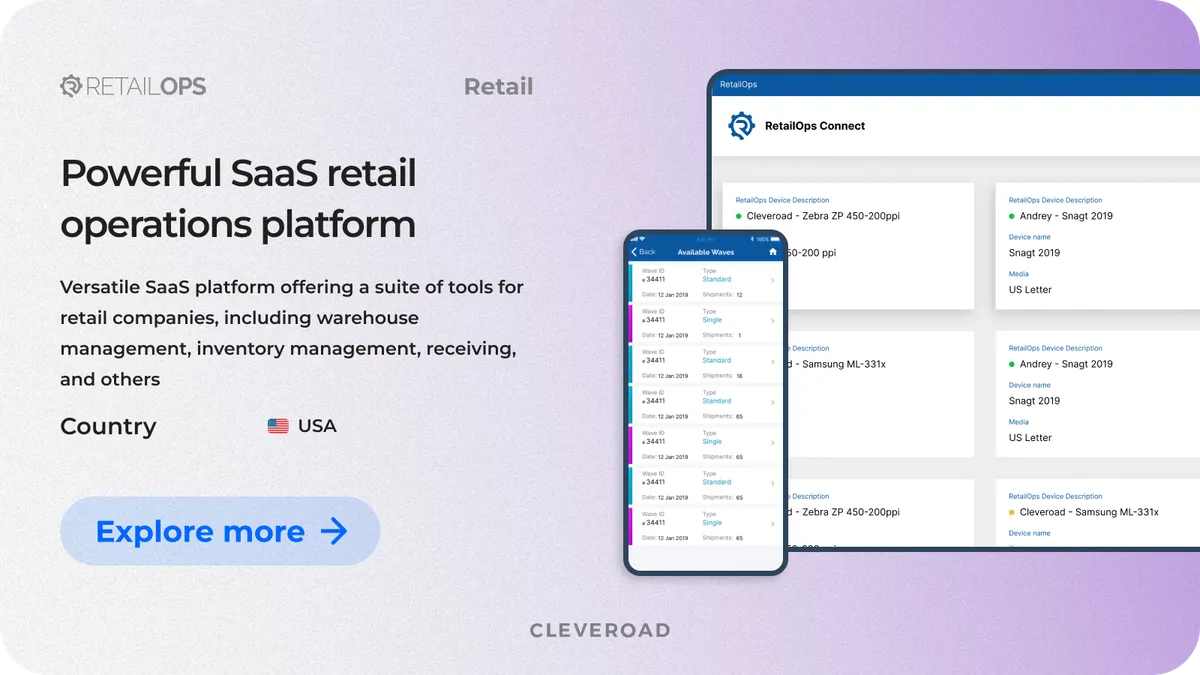
To demonstrate our experience in ERP software development for retail operations, here is a detailed overview of our recent case, RetailOps.
RetailOps is a US-based retail technology company that set out to build a unified SaaS platform for back-office retail operations. The founders could not find an existing solution that combined warehouse management, inventory tracking, receiving, and analytics into a single system. Their goal was to create a single operational platform to replace fragmented tools and support retail teams in their daily operations.
Cleveroad joined the project to reengineer and evolve the platform into a robust, scalable system. We redesigned the UI and UX to simplify complex retail workflows and rebuilt the mobile application natively in Swift, replacing the Cordova-based solution. Our team worked with the client’s existing backend and ensured seamless communication despite a significant time zone difference.
The retail operations management solution we've developed includes the following modules:
- Inventory management to track stock across warehouses and locations
- Warehouse management for receiving, storage, and shipping workflows
- Order and receiving modules to manage inbound and outbound inventory
- Hardware integrations, including barcode scanners and connected printers
- Reporting and analytics to monitor inventory movement, sales, and order status
As a result, our customer received a fully functional, mobile-first retail operations platform with a modern interface and reliable performance.


Implement ERP with a reliable vendor
With 15 years of experience in ERP development, Cleveroad will design and implement an ERP system tailored to your business workflows and ready for long-term stability and evolution
ERP software development refers to the whole process of planning, constructing, and supporting a centralized system that controls and connects the main business operations of the company. Building an ERP system consists of the unification of all the tools that are now working separately into a single platform for finance, inventory, sales, human resources, and reporting.
ERP software development services improve operational efficiency through centralizing data and standardizing workflows across departments. It reduces manual work and errors and supports faster decision-making. Also, ERP scales with business growth and adapts to changing operational needs.
Modern ERP software development costs typically range from $80,000 to $200,000+, depending on system complexity, integrations, and security requirements.
To choose the right ERP vendor, focus on these key criteria:
- Proven ERP experience with real projects that go beyond basic CRUD systems
- Strong business analysis and discovery process to prevent scope and cost overruns
- Expertise in modular and scalable architecture that supports long-term growth
- Integration experience with third-party systems such as CRM, accounting, and logistics tools
- Clear communication and transparency throughout development
- Post-launch support and scaling capabilities to evolve the ERP over time

Evgeniy Altynpara is a CTO and member of the Forbes Councils’ community of tech professionals. He is an expert in software development and technological entrepreneurship and has 10+years of experience in digital transformation consulting in Healthcare, FinTech, Supply Chain and Logistics
Give us your impressions about this article
Give us your impressions about this article
Comments
6 commentsAn Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software or system development helps organizations better manage their resources. ERPs connect every aspect of an enterprise. An ERP software system allows for better performance and project management that helps plan, budget, predict and accurately report on an organization's financial health and processes. Thanks for sharing this Informative article.
Thanks for this great post, very informative and helpful for readers of all backgrounds. ERP systems are very beneficial however some people may prefer to pay for one built for them than to build it themselves.
I'm an owner of a small retail network. We use ERP systems to control internal processes. We use third-party solution (don't want to disclose the vendor), but I'm planning on developing my own. Thanks
Astonishing content
Thanks for the efforts you put in your article. It would be interesting to know more about integrations of third-party software into custom ERP system. Keep on keeping on!
Great post! Thanks for your work